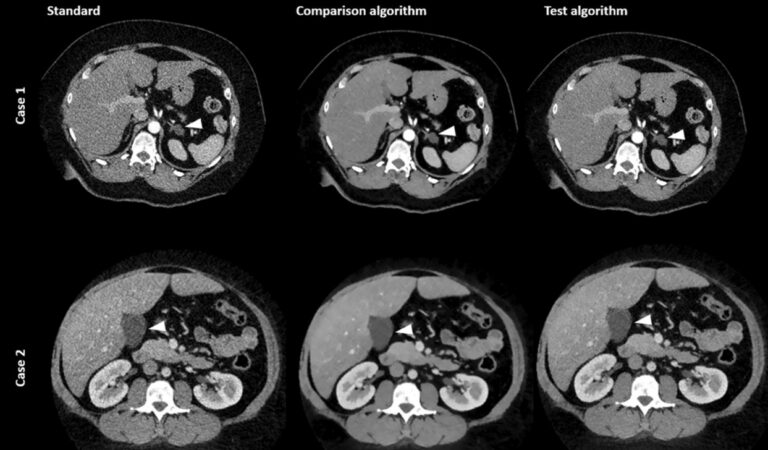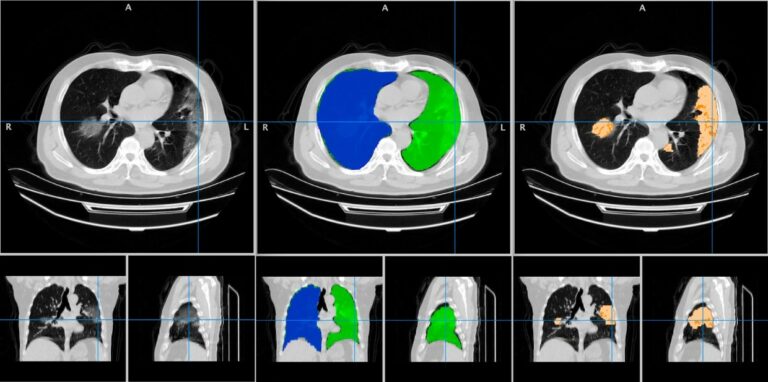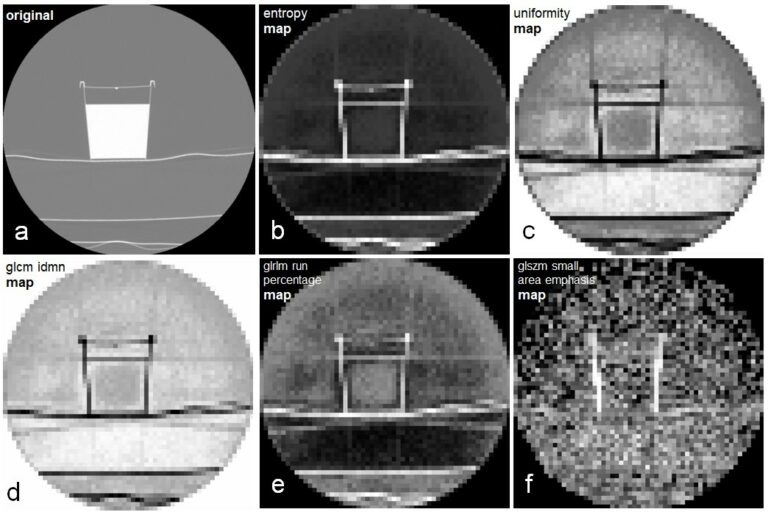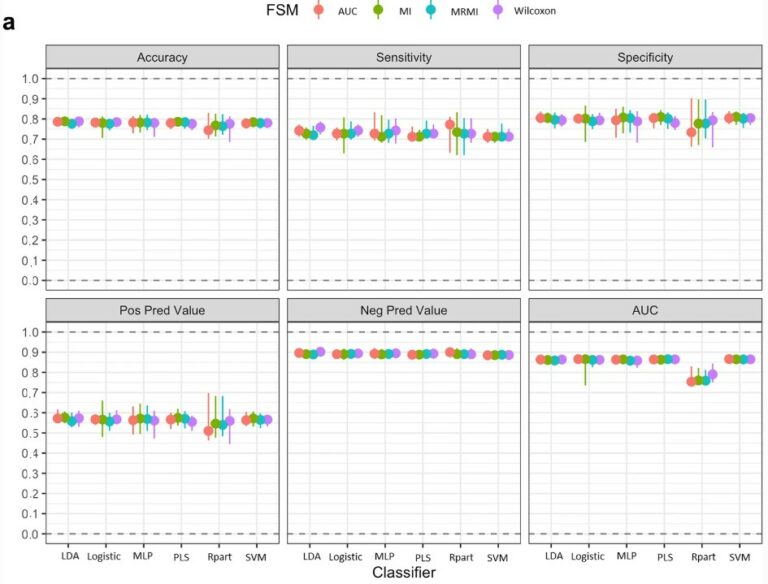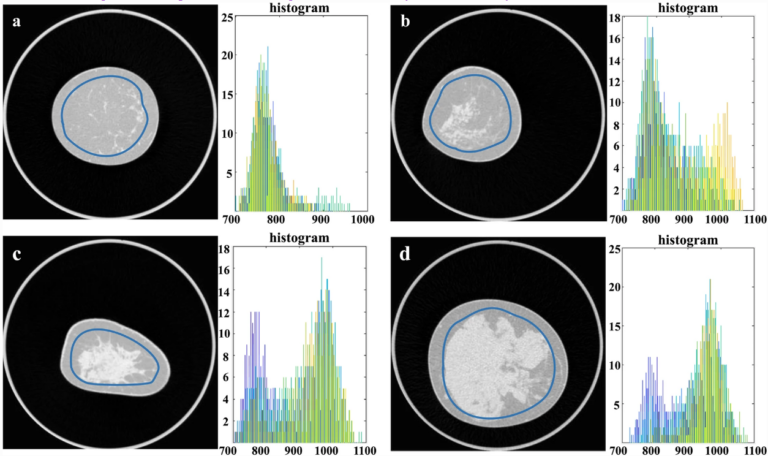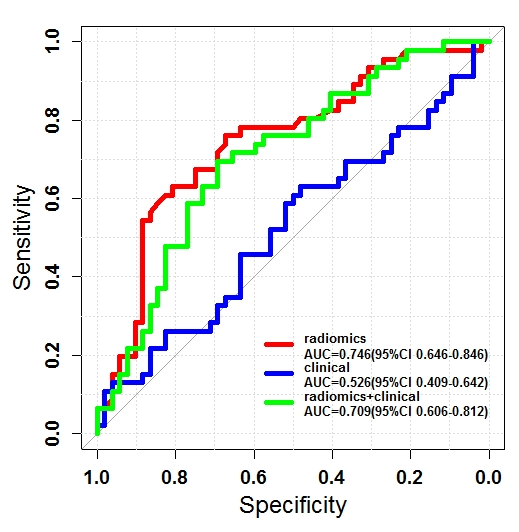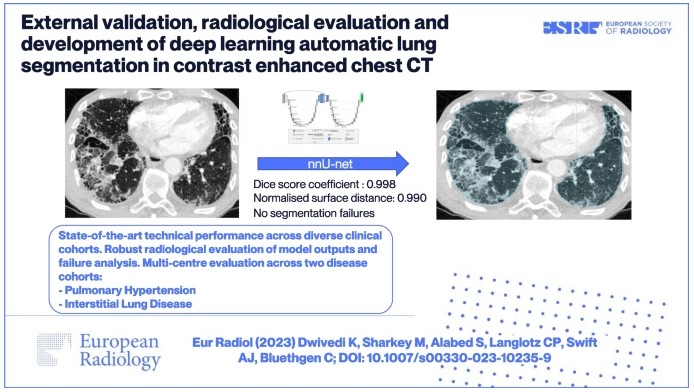
External validation, radiological evaluation, and development of DL lung segmentation in chest CT
The authors of this study developed a 3D nnU-Net-based model for automatic lung segmentation in computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) imaging that was found to be highly accurate, clinically evaluated, and externally tested in patient cohorts with a spread of lung disease. Key points Article: External validation, radiological evaluation, and development of deep learning automatic lung segmentation in contrast-enhanced chest CT