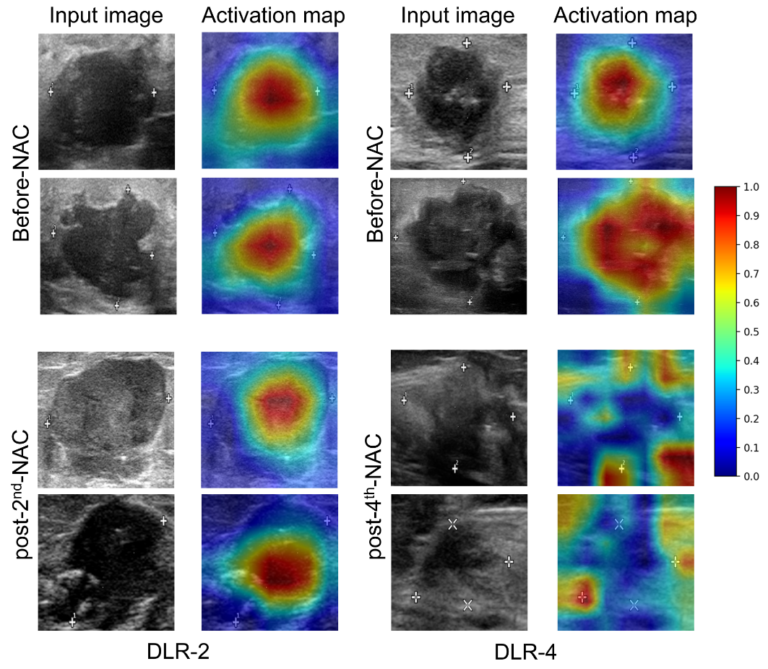
Deep learning radiomics in prediction of NAC response
For breast cancer, the standard of treatment for most patients is neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), but response rates may vary among patients, causing delays in appropriate treatment. The authors of this prospective study aimed to investigate the feasibility of deep learning radiomics (DLR) in the prediction of NAC response at an early stage of breast cancer treatment. The authors found that