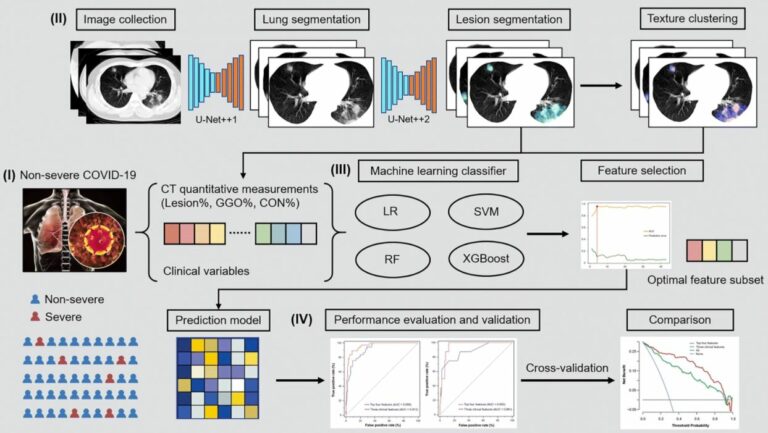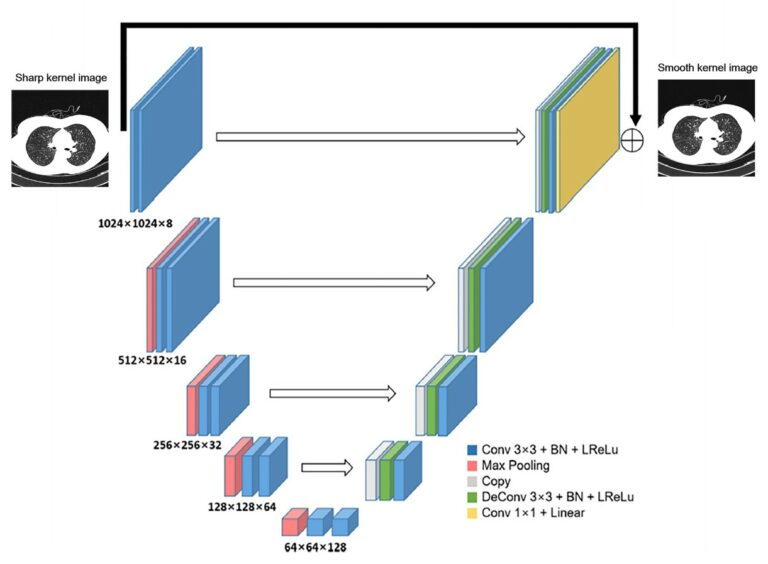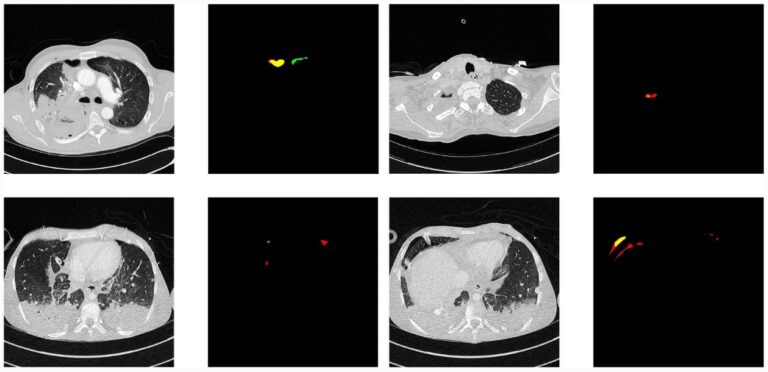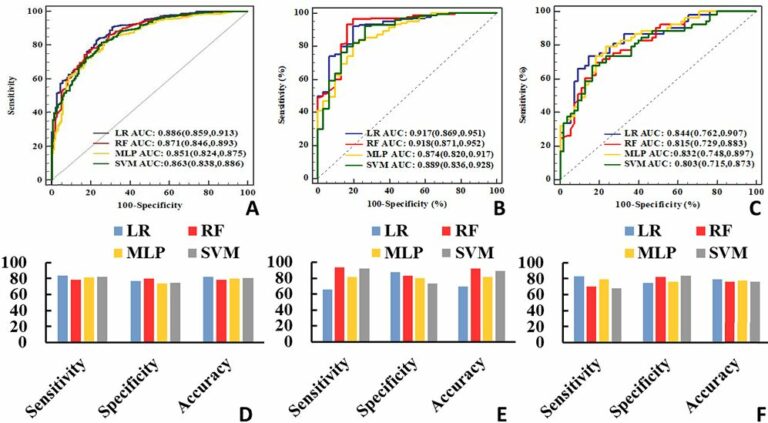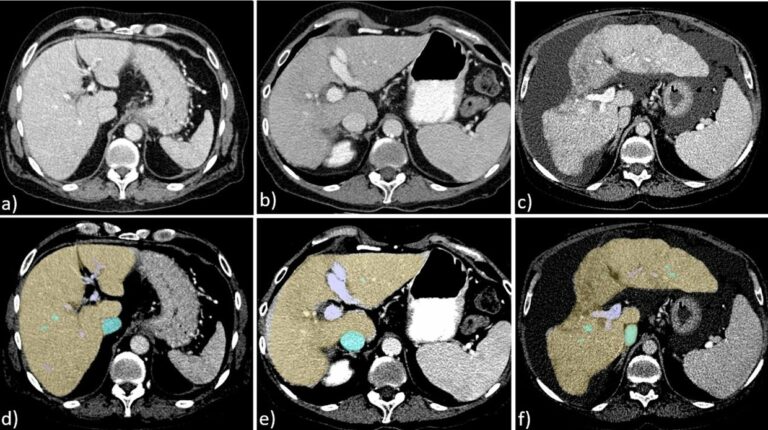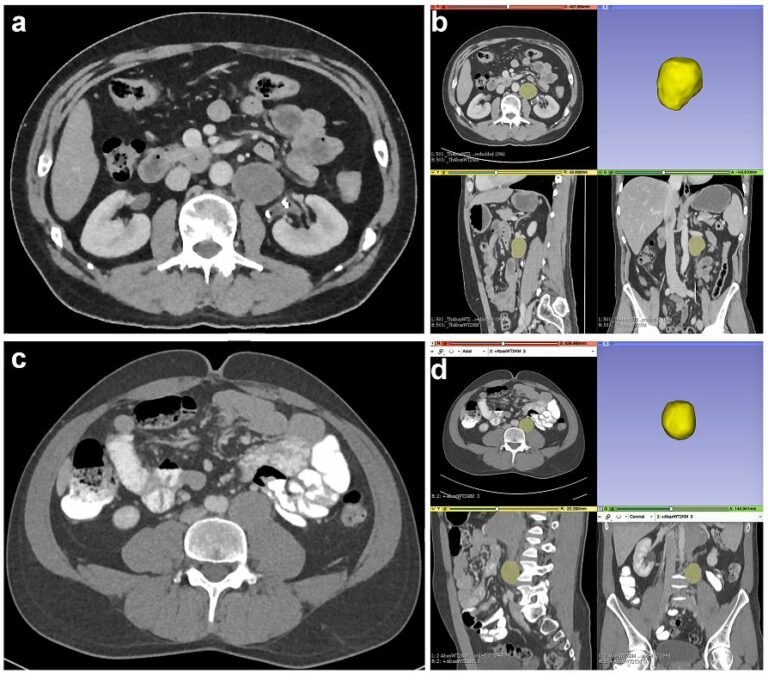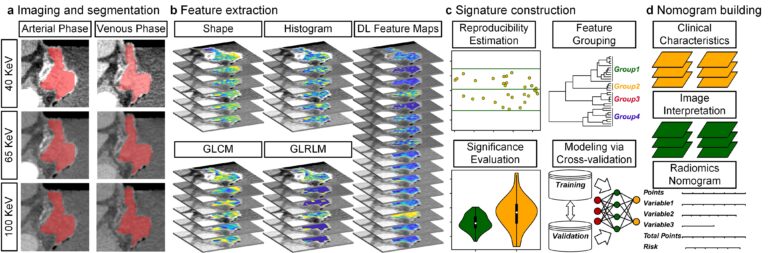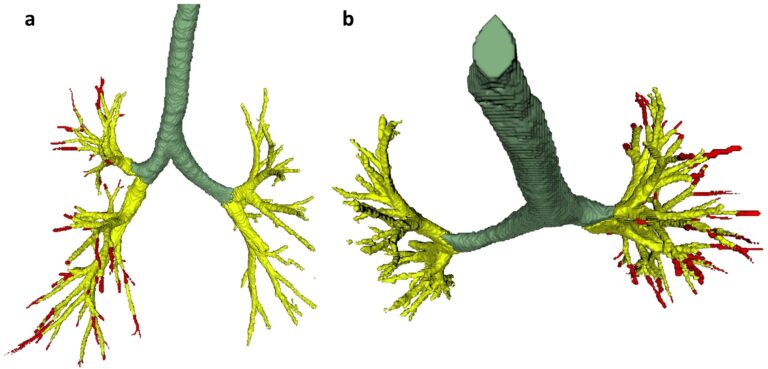
Creating a training set for AI from initial segmentations of airways
An important challenge in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for medical image segmentation tasks is the lack of high-quality, scan protocol-specific datasets. AI performs best on narrow tasks with homogenous specifications. Thus, pre-trained models may be inadequate for use in centre-specific studies if the scan protocols do not match. For the airway segmentation task in the Imaging in Lifelines