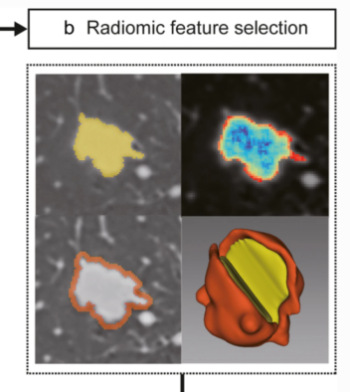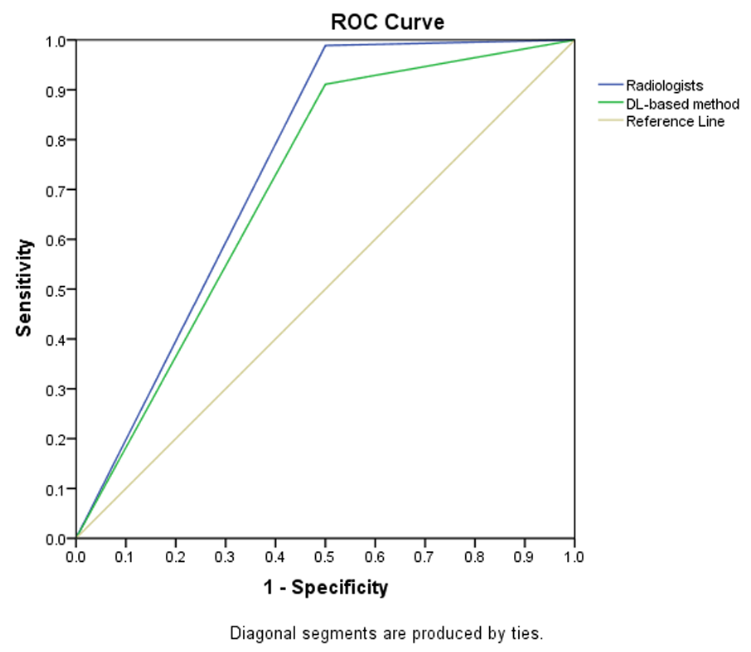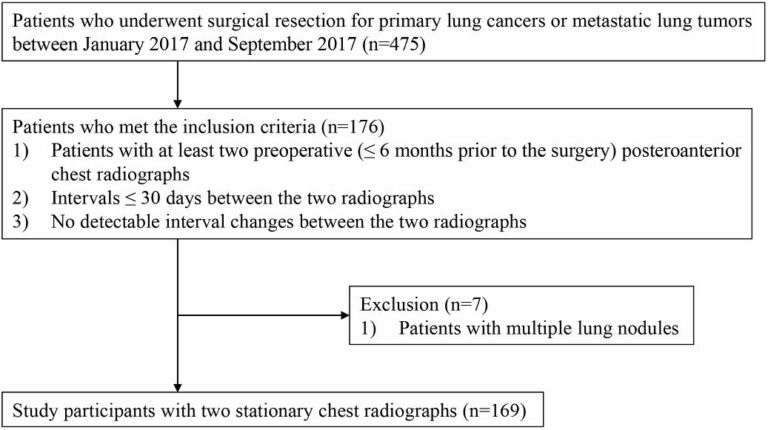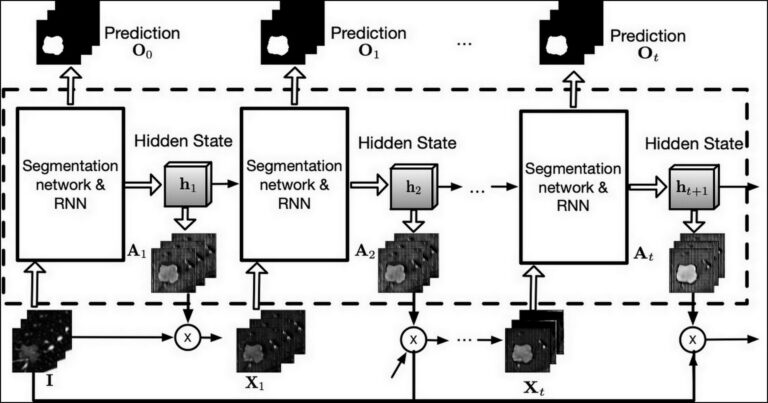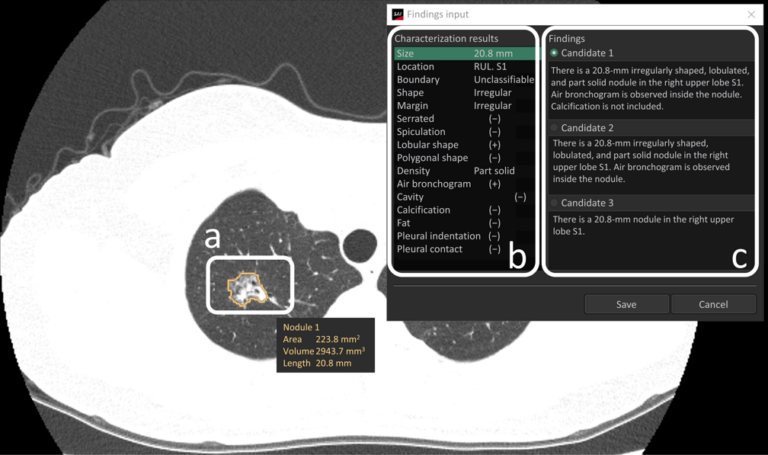
Radiologists with and without deep learning–based computer-aided diagnosis
When radiologists encounter pulmonary nodules/masses in computed tomography (CT) images, they diagnose malignancy based on lesion characteristics (e.g., spiculation and calcification). However, accurate characterization requires careful observation and can be difficult, especially for inexperienced radiologists. In addition, the assessments may vary among radiologists, resulting in the low reproductivity of findings. We investigated if commercially-available deep learning (DL)-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD)