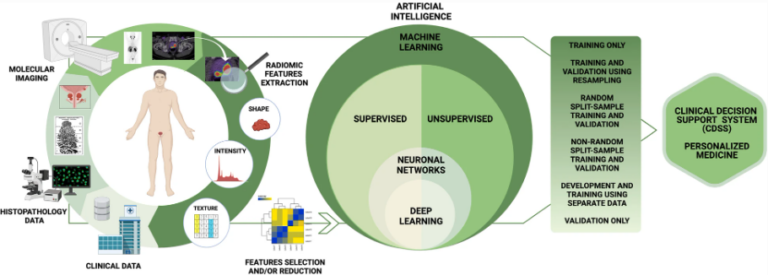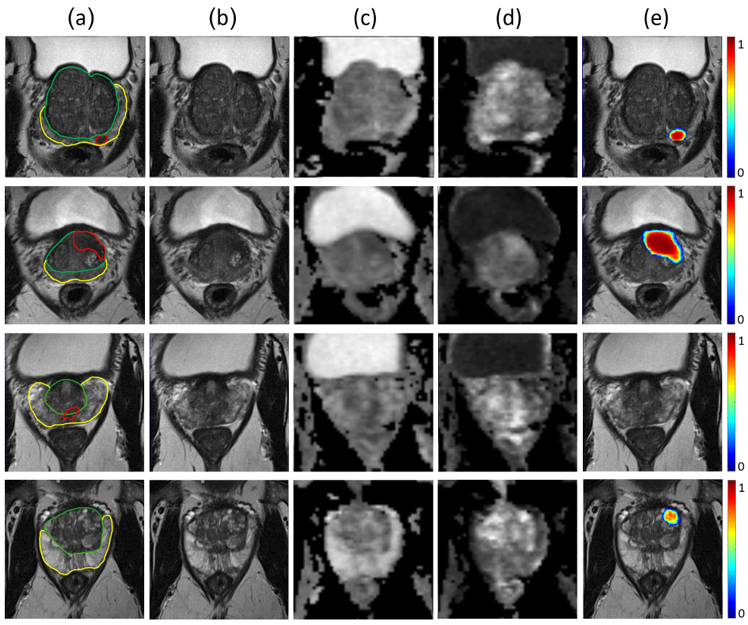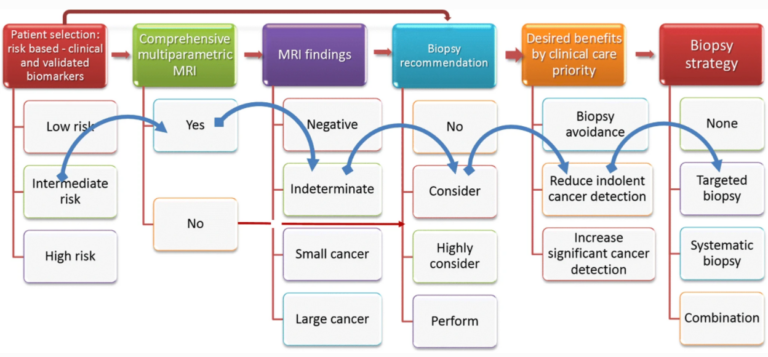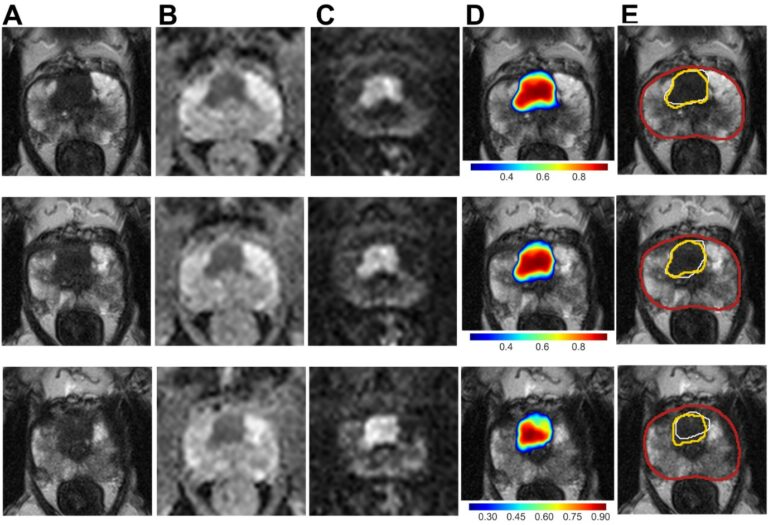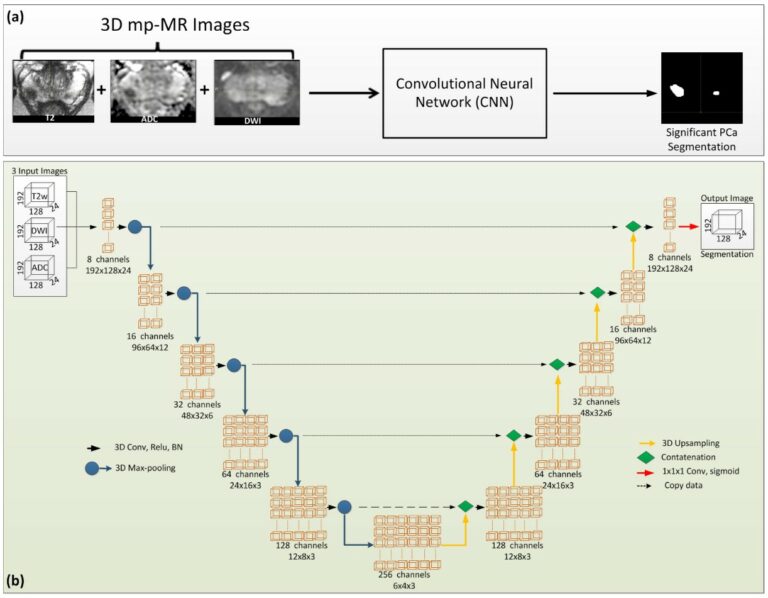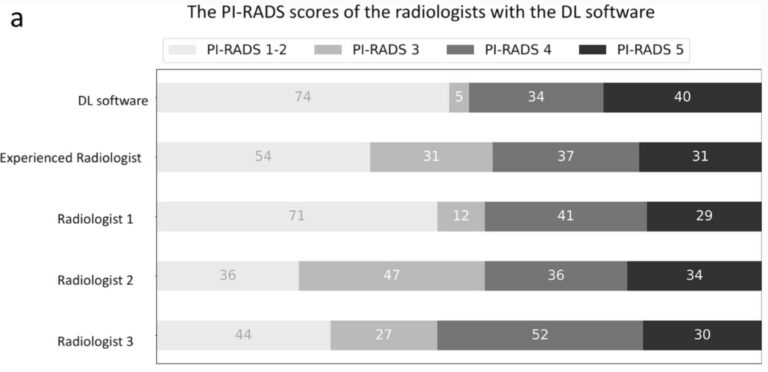
Does deep learning improve the consistency and performance of radiologists in assessing bi-parametric prostate MRI?
Our study aimed to evaluate whether deep learning (DL) software could enhance the consistency and performance of radiologists in assessing bi-parametric prostate MRI scans. Intriguingly, our findings revealed that the DL software did not significantly improve the Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scoring consistency or the detection performance of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) among radiologists with varying levels