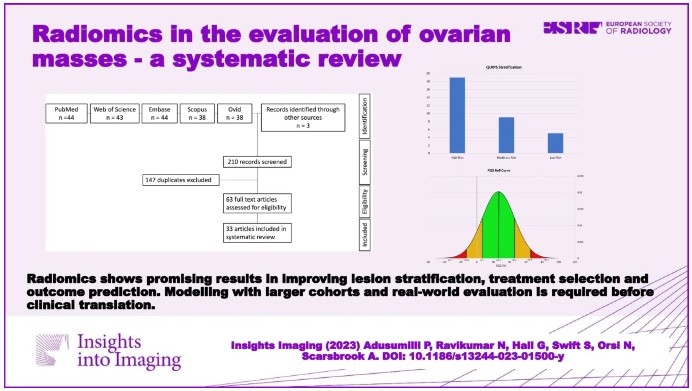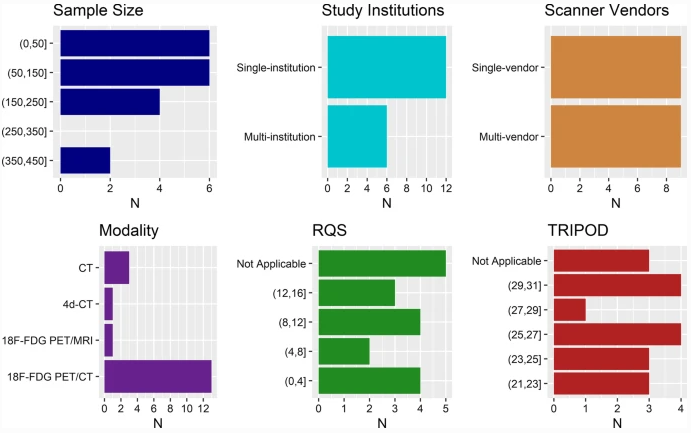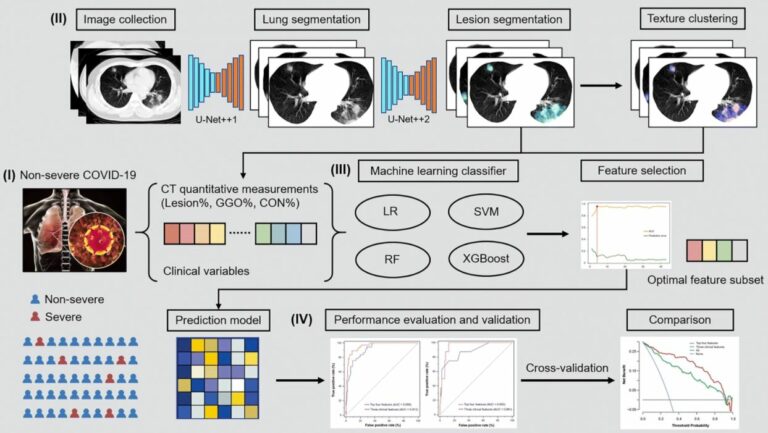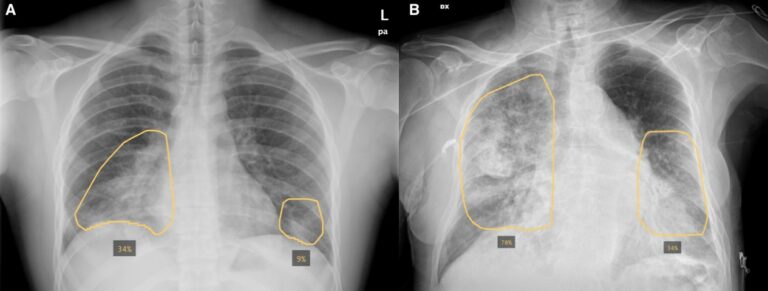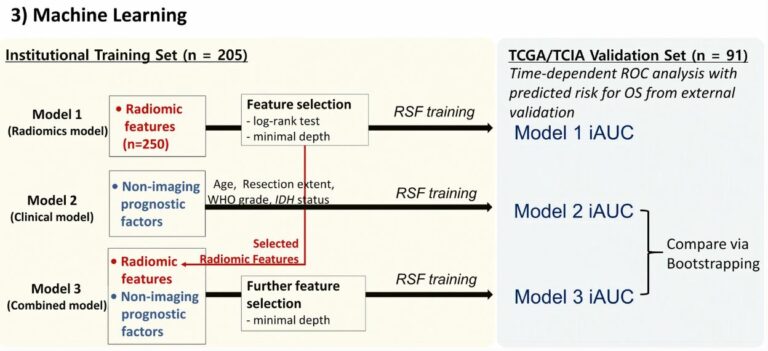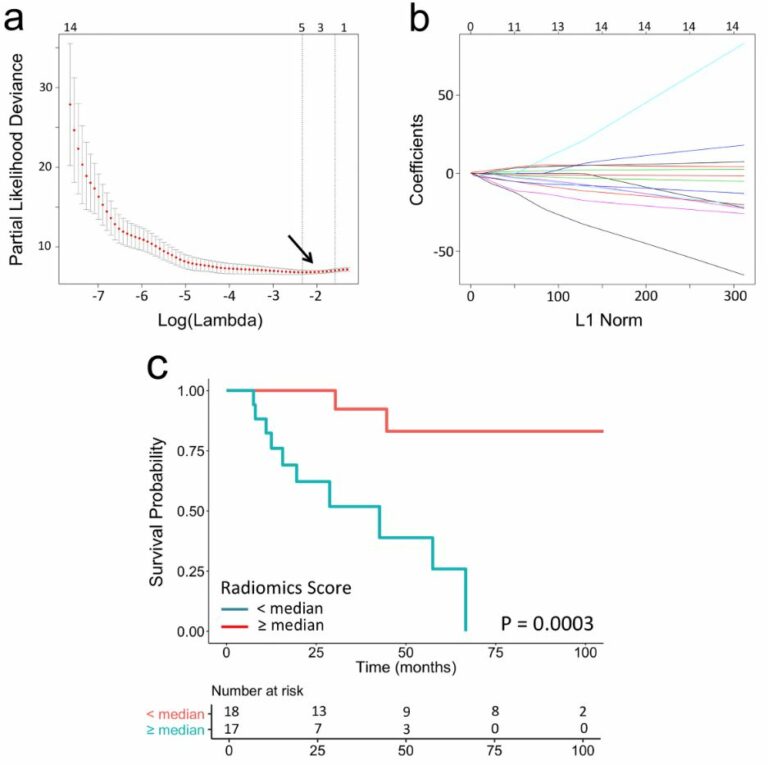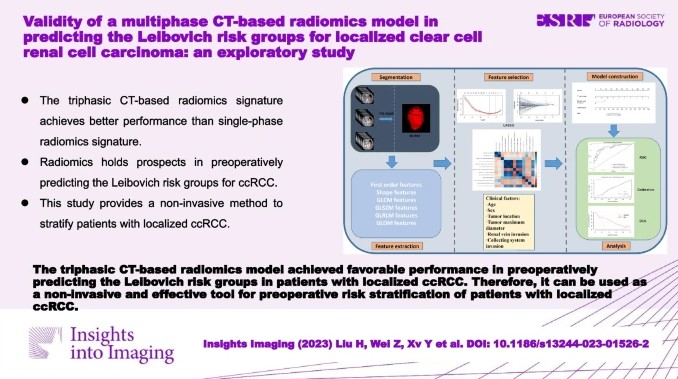
New radiomics model to predict the Leibovich risk groups for ccRCC patients
This study developed and validated a triphasic CT-based radiomics model, which incorporated radiomics features and significant clinical factors, for preoperative risk stratification of patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). The model showed a favorable performance in preoperatively predicting the Leibovich low-risk and intermediate-high-risk groups in localized ccRCC patients. The authors determined that this model can be used