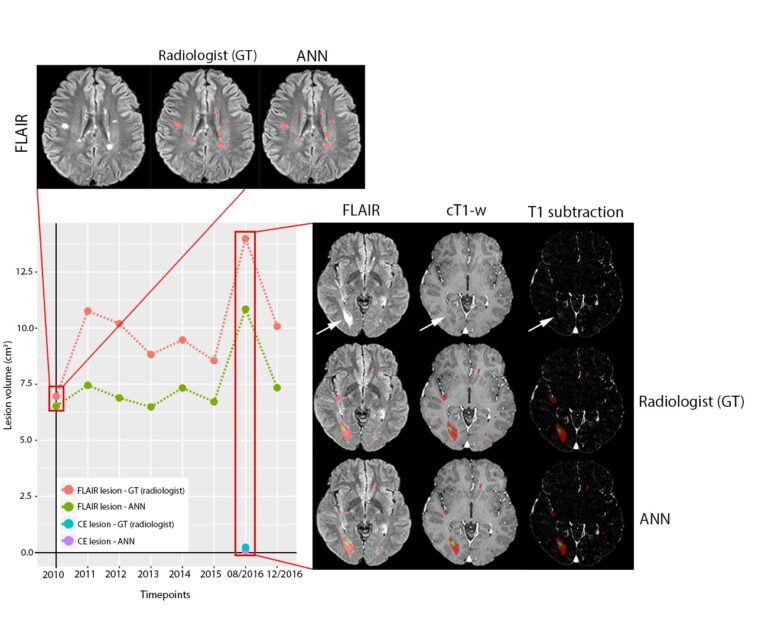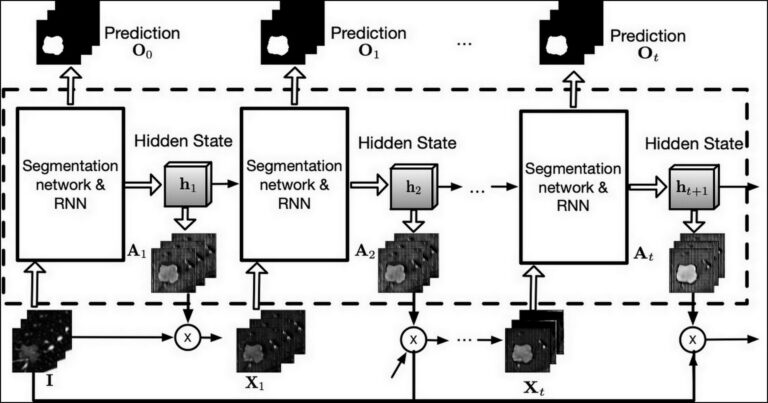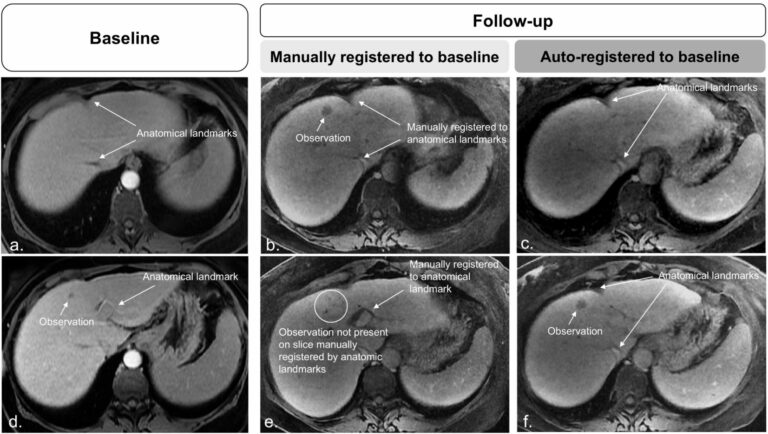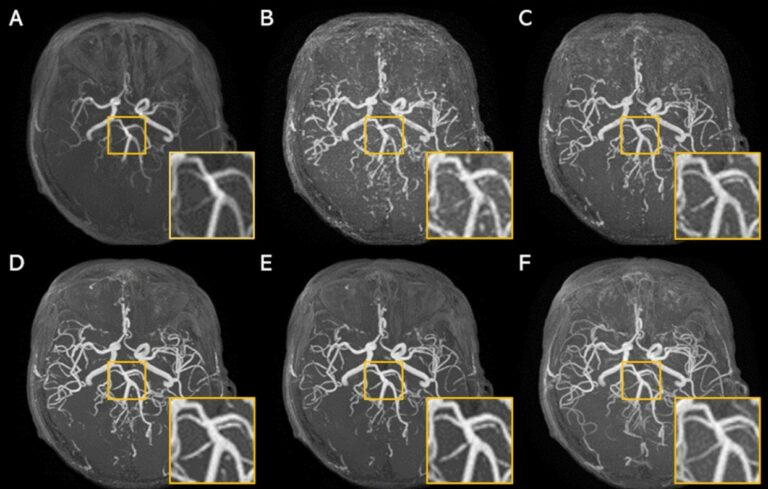
Super-resolution application of GAN on brain time-of-flight MR angiography
This study aimed to develop a generative adversarial network (GAN) model to improve the image resolution of brain time-of-flight MR angiography (TOF-MRA), as well as evaluate the image quality and diagnostic utility of the reconstructed images. The results showed that an optimized GAN could significantly improve the image quality and vessel visibility of low-resolution 3D TOF-MRA while maintaining equivalent sensitivity