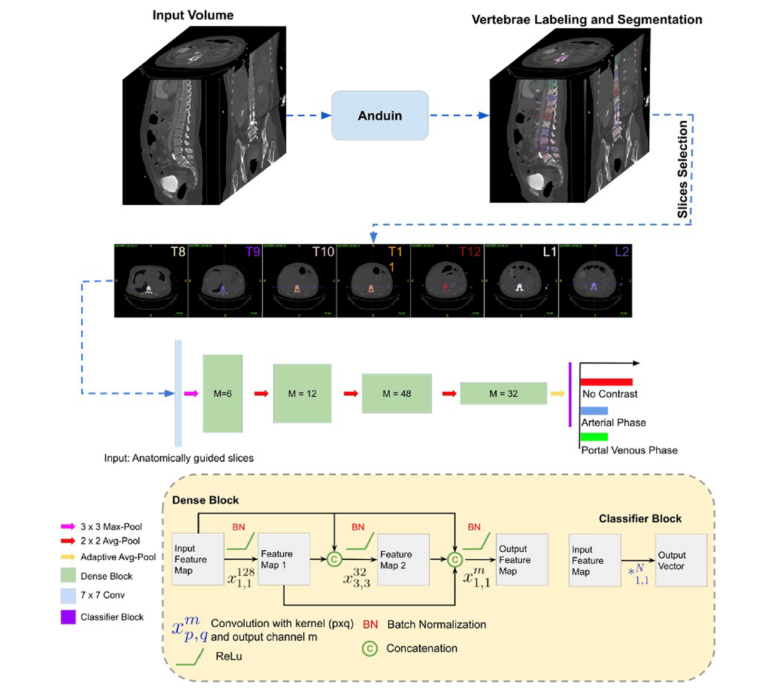
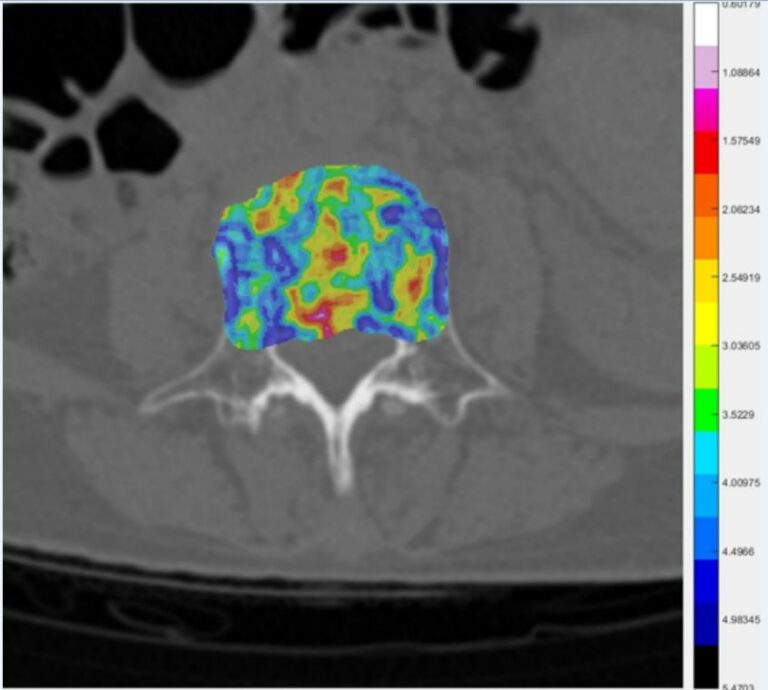
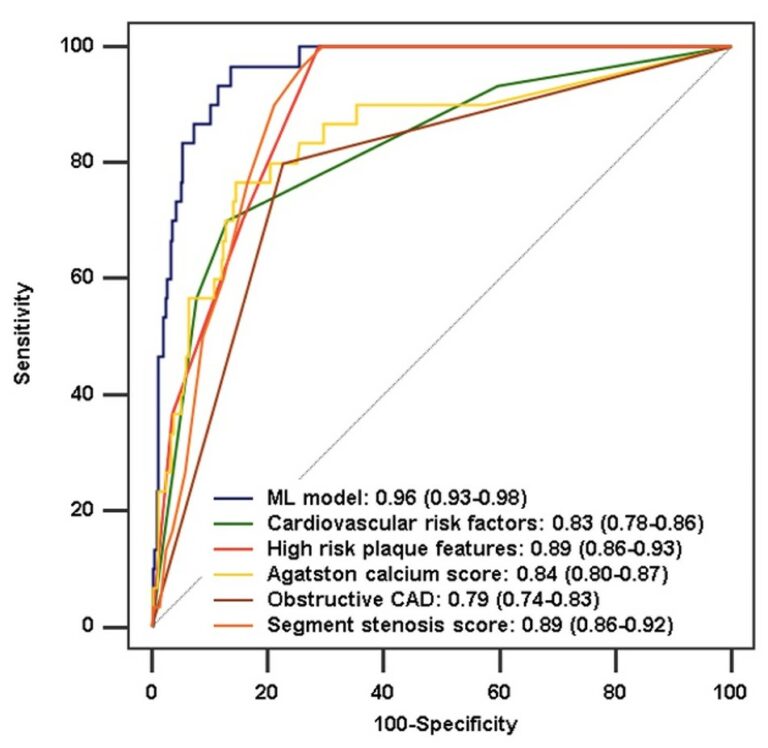
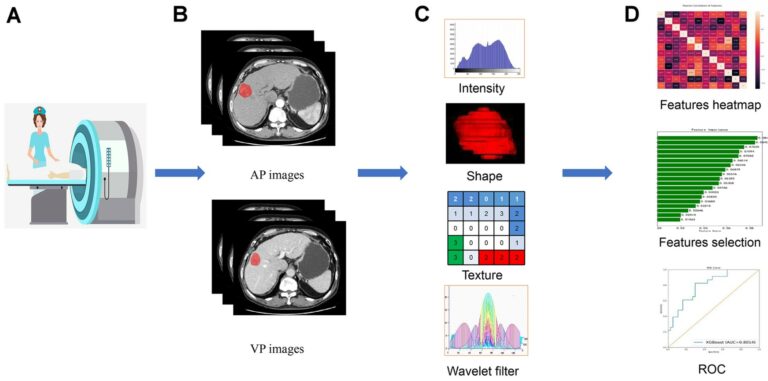
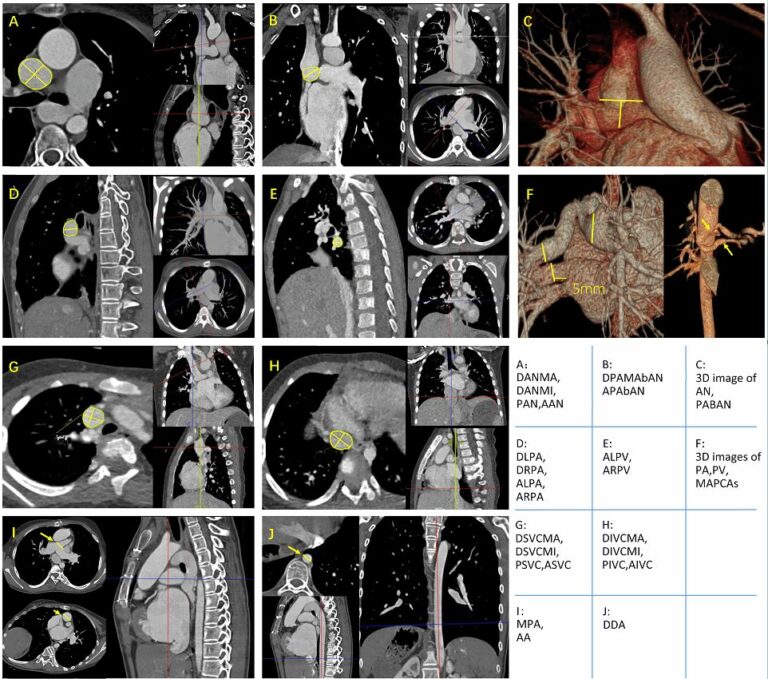
Deep learning image reconstruction to improve accuracy of iodine quantification and image quality in abdomen dual-energy CT
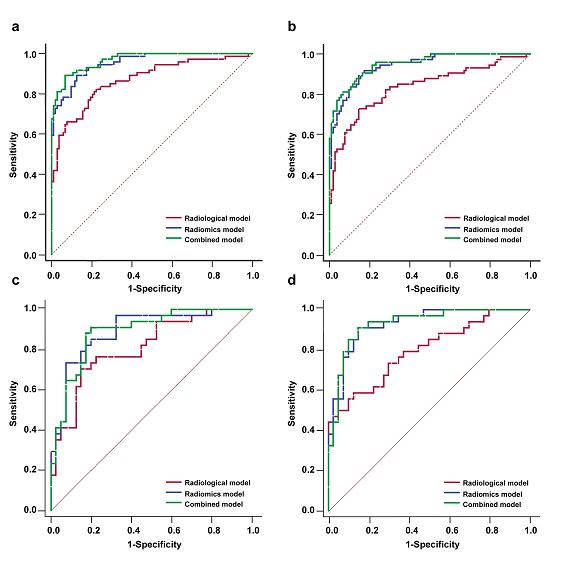
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of deep learning image reconstruction (DLIR) on the accuracy of iodine quantification and image quality of dual-energy CT (DECT) compared to other reconstruction algorithms. The authors showed that the DLIR algorithm reduced image noise and variability of iodine concentration values when compared with other reconstruction algorithms. Key points In the