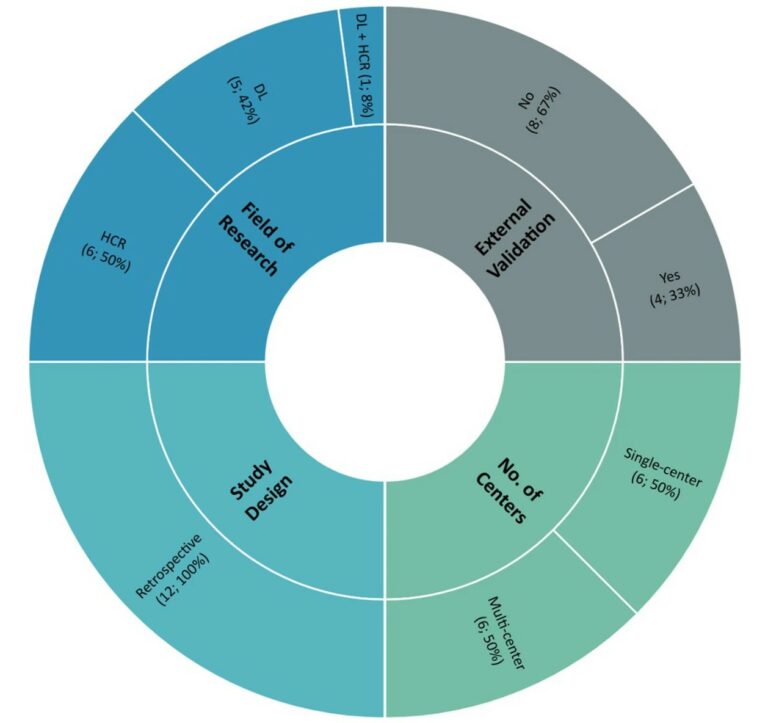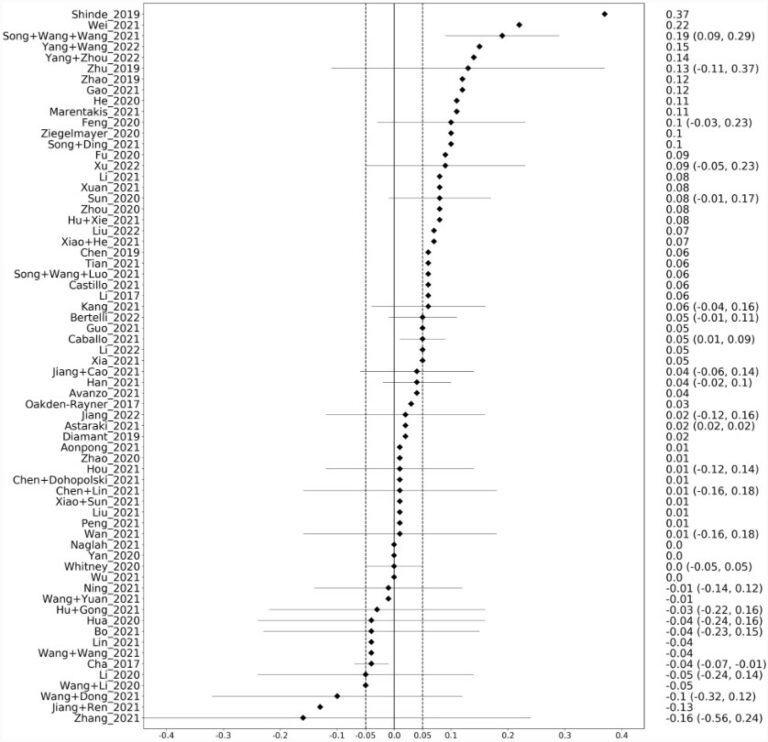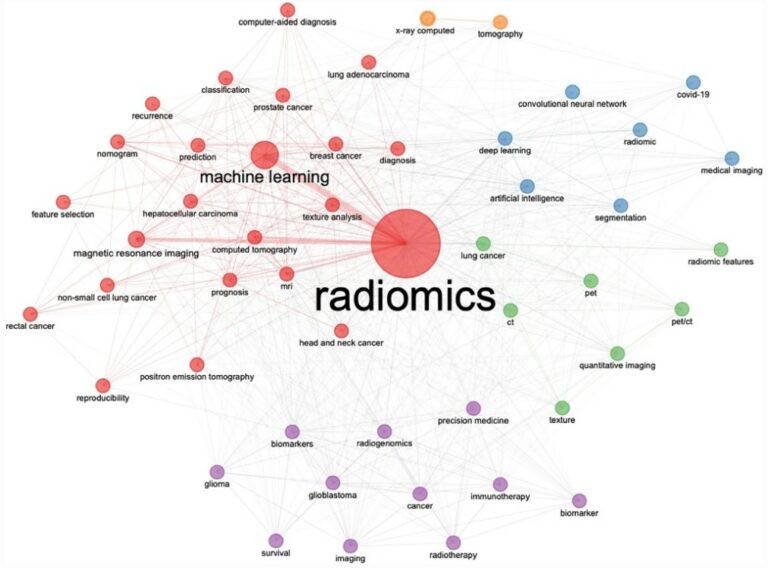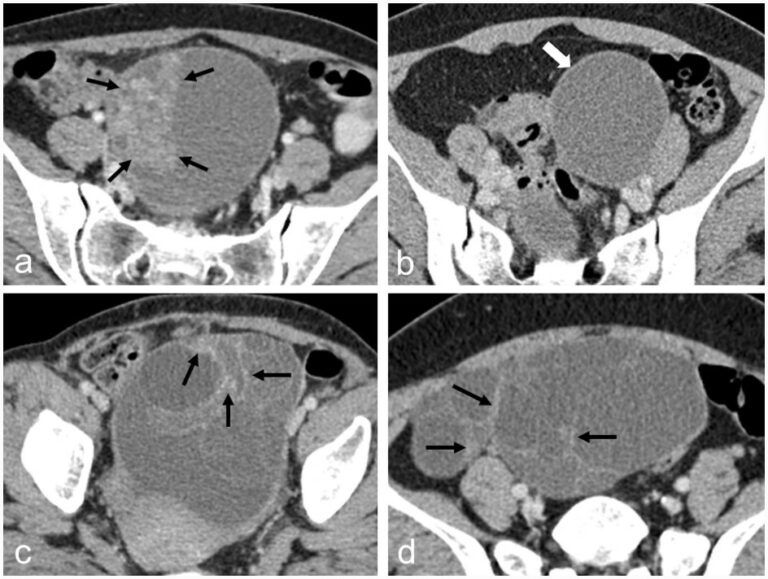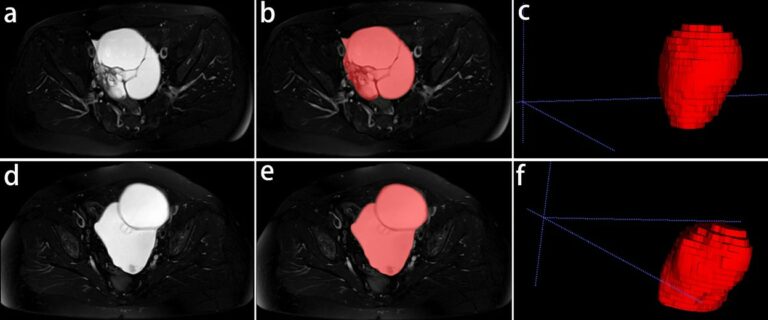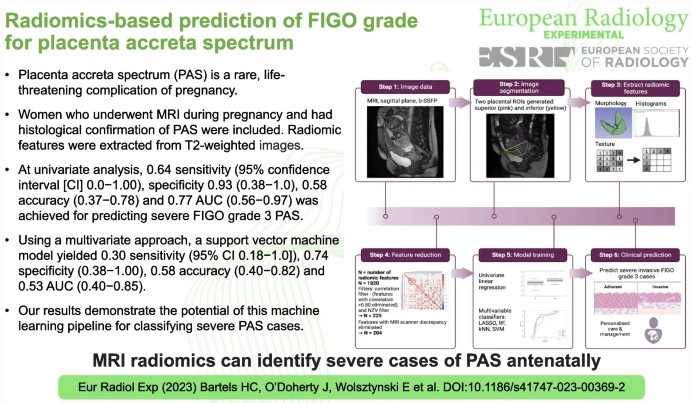
Radiomics-based prediction of FIGO grade for placenta accreta spectrum
Placenta Accreta Spectrum (PAS) is a serious, life-threatening pregnancy complication. Although rare, as more women are giving birth by Caesarean section, PAS is becoming more common. The most important factor in improving outcomes for mothers and babies is the detection of PAS during pregnancy to ensure the appropriate multi-disciplinary team care is implemented for the pregnancy and birth. However, up