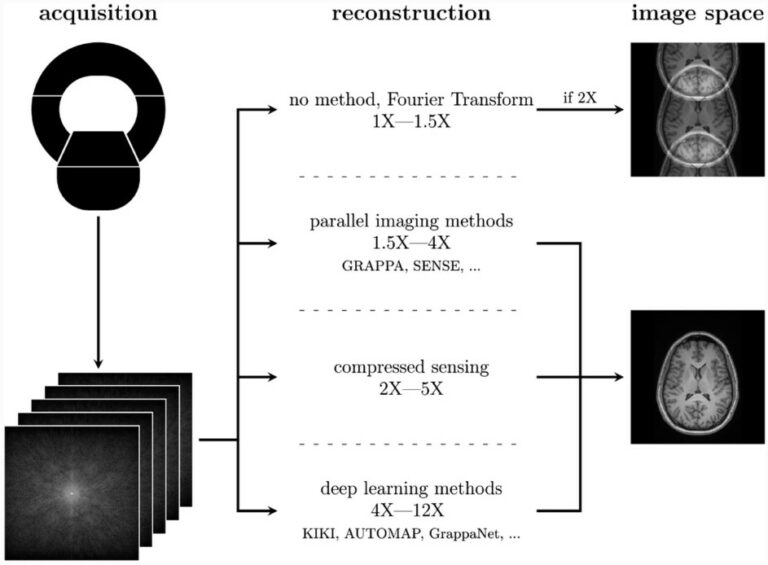
Complexities of deep learning-based undersampled MR image reconstruction
Recent advances in AI have led to deep learning-based MR undersampled image reconstruction methods showing more speed-ups compared to traditional algorithms. MR undersampling is an excellent way to reduce scan time but can negatively impact image quality. Our literature review aims to inform a broader audience about this complex topic. This highly multidisciplinary science requires the informed input of many