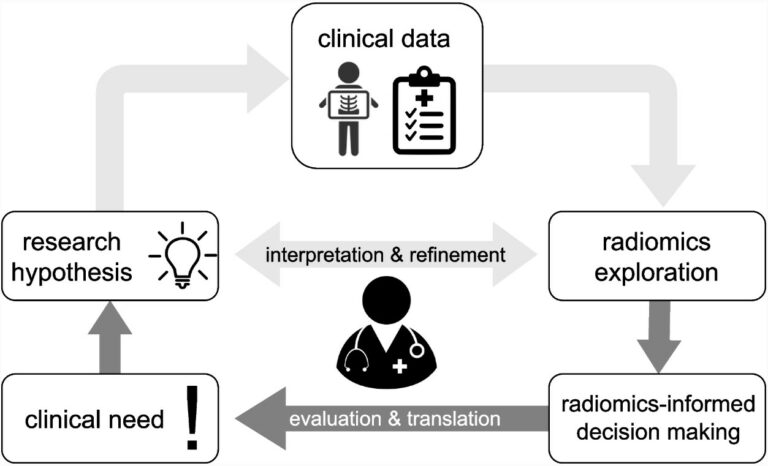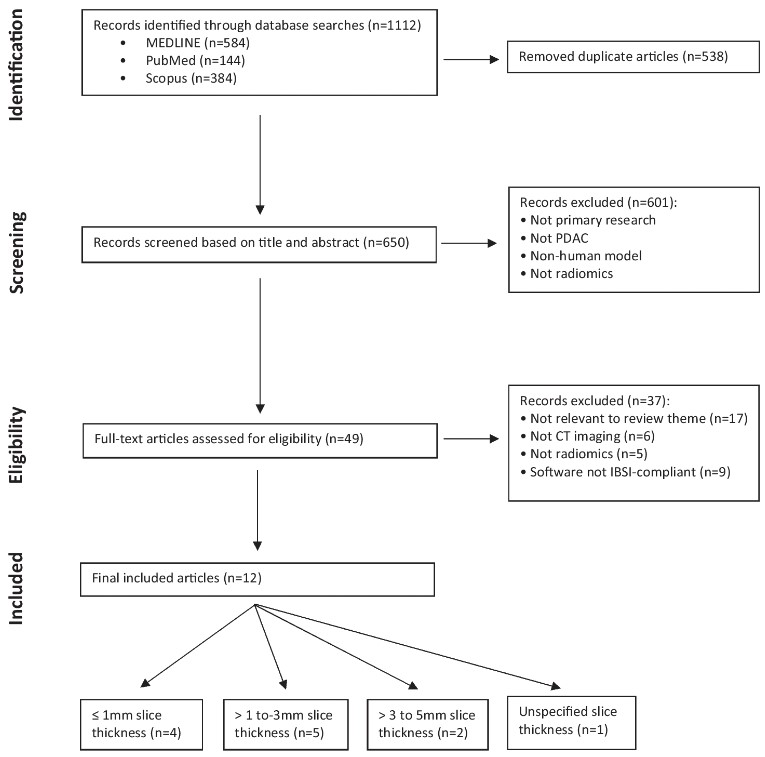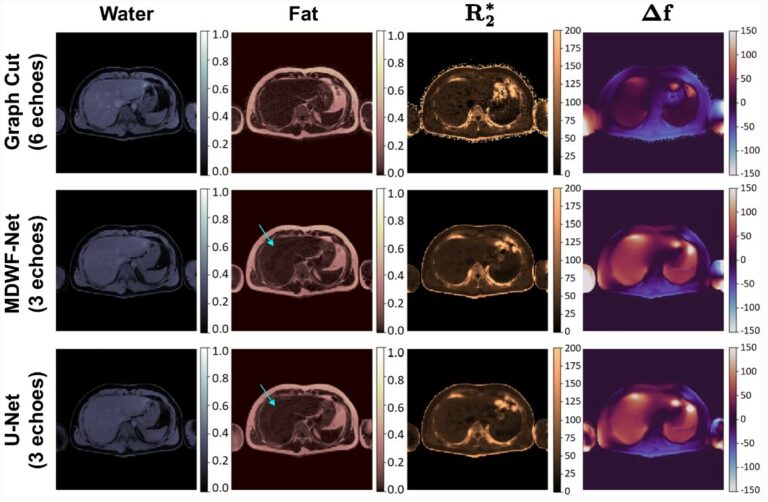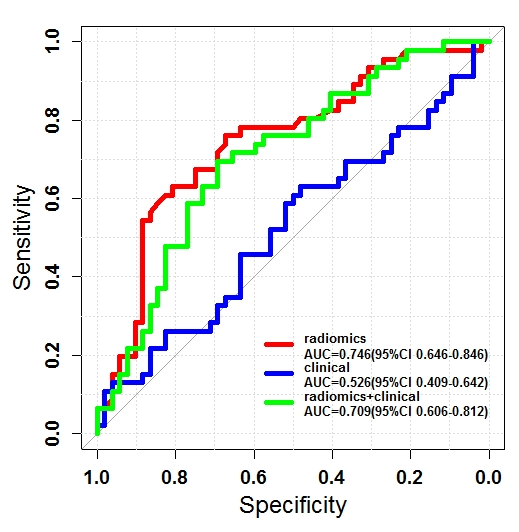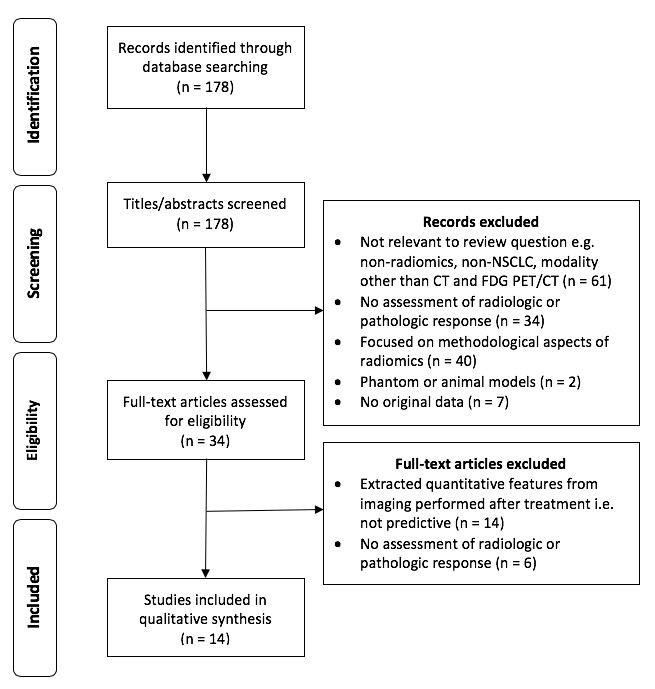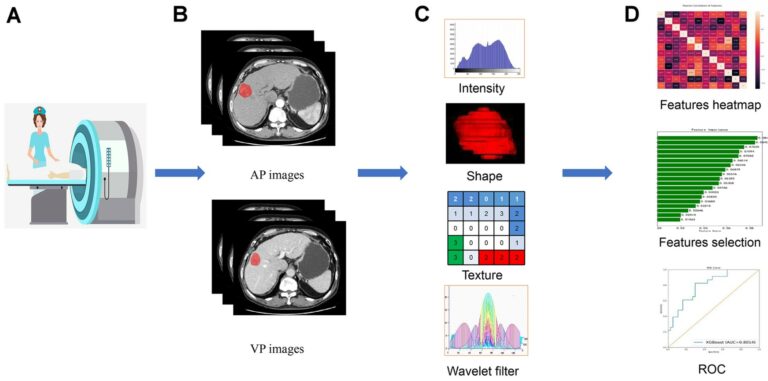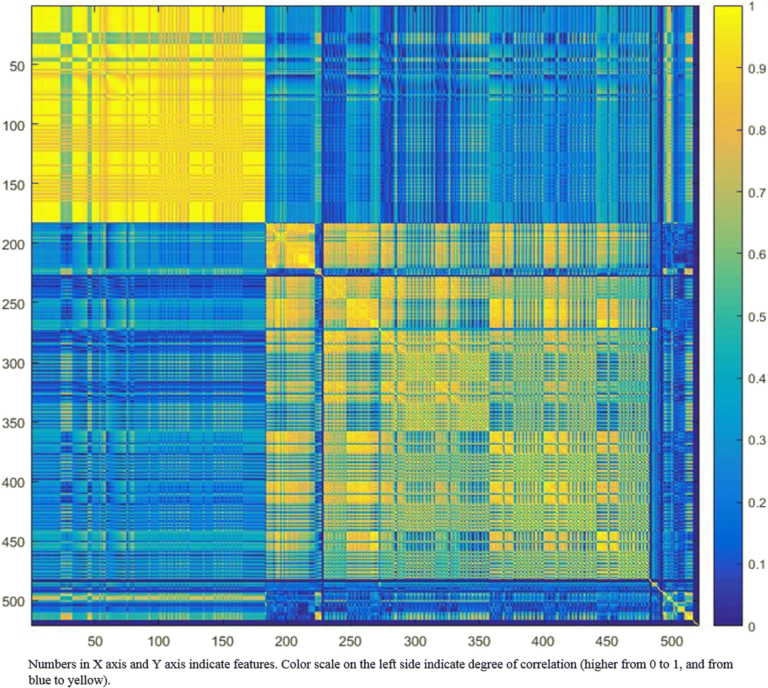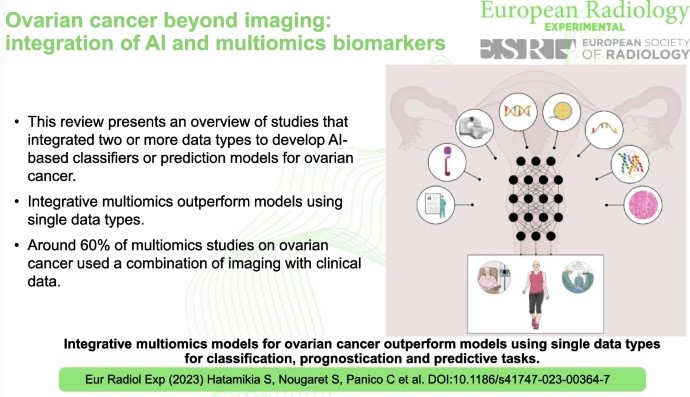
Ovarian cancer beyond imaging: integration of AI and multiomics biomarkers
Ovarian cancer, often referred to as the “silent killer”, tends to show inconspicuous symptoms in the early stages, making timely diagnosis difficult. Detecting ovarian cancer at an early stage significantly increases the chances of effective treatment and therefore the chances of survival. This review study has shown that AI-based tools that rely on the integration of multi-omics data perform better