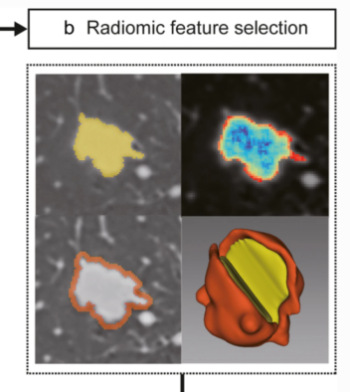
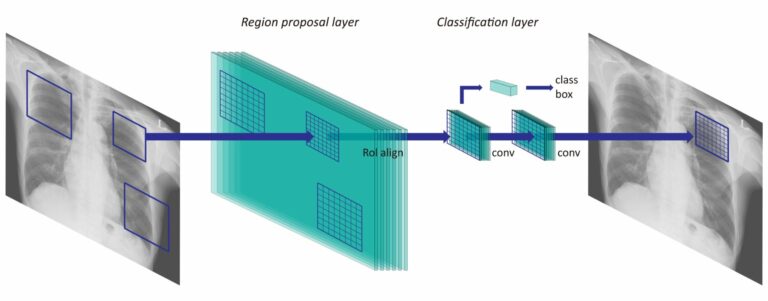
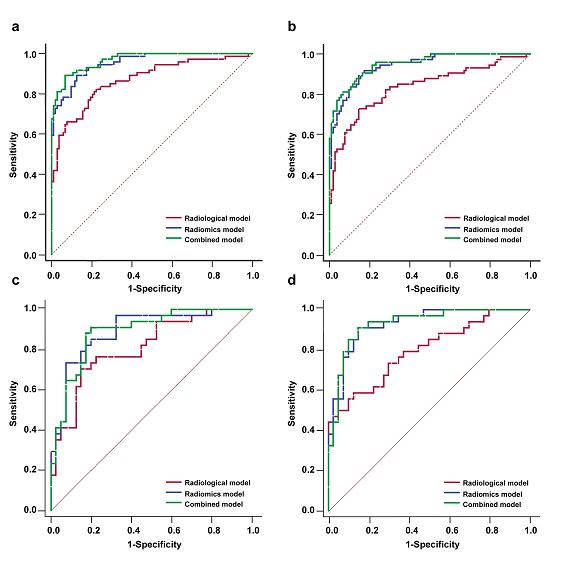
Radiologists’ performance improved by algorithmic transparency and interpretability measures
This study’s aim was to evaluate the perception of various types of artificial intelligence-based assistance and the interaction of radiologists with the algorithm’s predictions and certainty measures. As was consistent with previous research, the authors determined that human performance was superior to both groups when combined with AI. They also found an increase in trust in the algorithm’s performance when