In radiomics, the main goal is to extract quantitative features from medical data to train a predictive model using machine learning techniques. Contrary to statistics, radiomics is data-driven; thus, there is a certain tendency to use as many features as possible. To achieve this, preprocessing filters are often applied; for example, a Gaussian filter smooths the image and thus removes noise, and a wavelet filter decomposes the image into spectral frequencies that features can utilize.
Yet, this approach comes with a price. Many of these features will be irrelevant and redundant, complicating the training. It is well known that increasing the number of features comes hand in hand with a high risk of overfitting, especially if there are many more features than samples, which is often the case in radiomics. This effect is also called the curse of dimensionality. Therefore, adding many features could decrease predictive performance, contradicting the original intention.
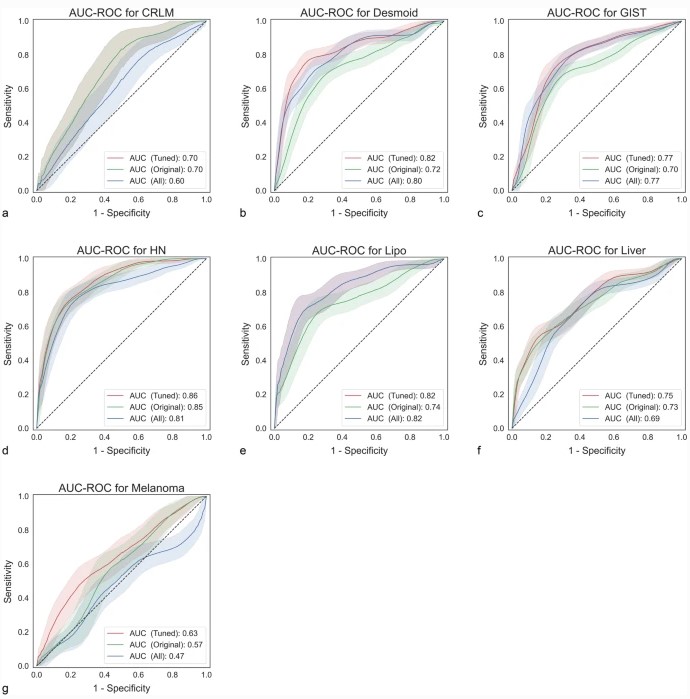
Our study tested the effect of adding preprocessed features on predictive performance. On seven publicly available datasets, we compared the impact of eight different preprocessing filters on the area-under-the-curve (AUC). We found that using preprocessing filters can result in significant improvements of up to +0.08 in AUC compared to using only the original features. However, though it also decreased performance (up to -0.10) on some data sets, these drops were not statistically significant. Tuning the set of preprocessing filters always led to increased performance, although failing to reach statistical significance.
Based on these results, we recommend using all preprocessing filters; using too few features might hurt predictive performance. Ideally, the set of features should be tuned during training.
Key points
- Modeling using all preprocessed features did not reduce the predictive performance compared to the original (not preprocessed) set.
- Tuning image processing filters during cross-validation improves the performance slightly.
- Using all preprocessed features seemed to be more helpful for datasets with larger sample size.
- Pairwise Pearson correlations of preprocessed feature sets were high (r > 0.49).
Article: The effect of preprocessing filters on predictive performance in radiomics
Authors: Aydin Demircioğlu