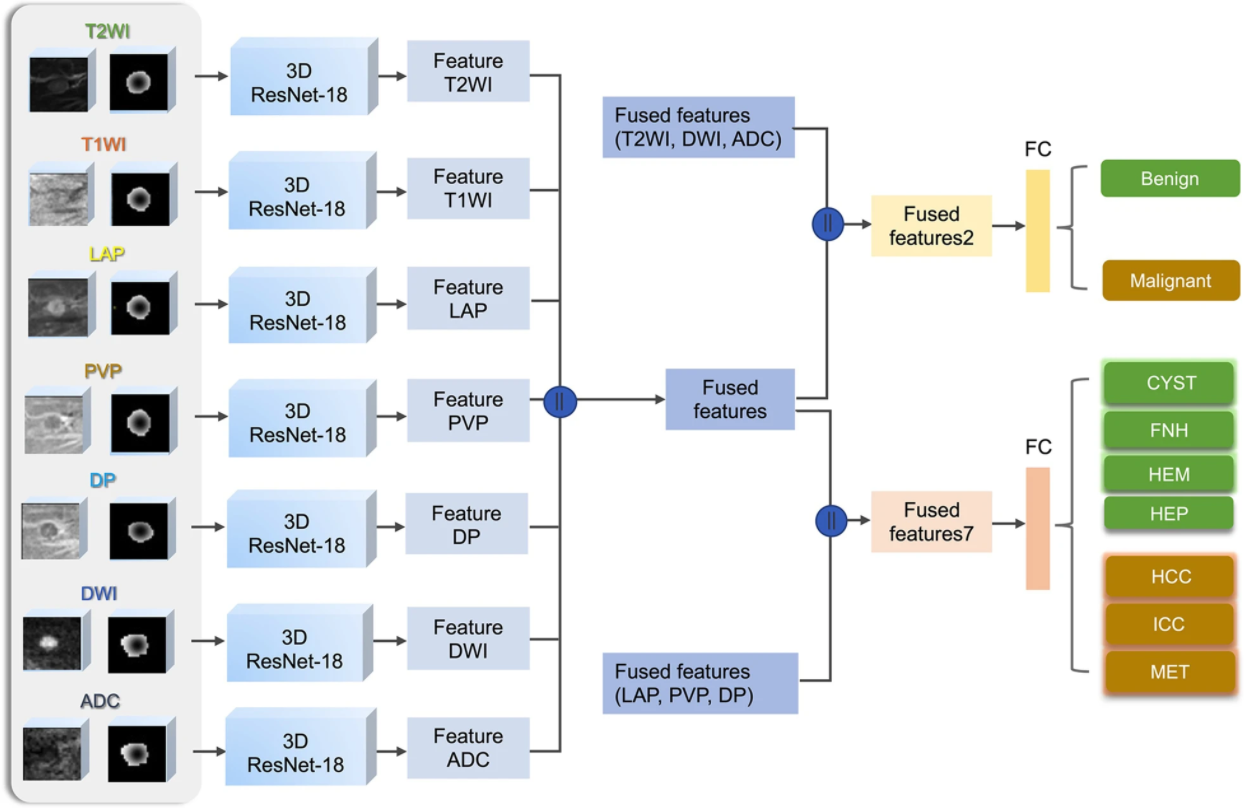
We investigated a saliency-based 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify seven categories of common focal liver lesions and validated the model performance. This retrospective study included 557 lesions examined by multisequence MRI. We found that this interpretable deep learning model showed high diagnostic performance in the differentiation of common liver masses on multisequence MRI.
A few important notes on our study:
- The model accuracy of the seven-way classification was higher than that of the radiology residents and general radiologists but lower than that of the academic radiologists.
- Saliency maps could explain model decision-making and let radiologists and clinicians verify the diagnosis.
- AI has the potential to relieve physicians and staff of the need to carry out the primary diagnosis by automating the process, thereby lightening the burden on radiologists.
Key points
- AI has the potential to relieve physicians by automating the process.
- This model could accurately classify common liver masses on multisequence MRI.
- Different MRI scanners and liver background did not affect the model performance.
- Saliency maps could explain model decision-making and let radiologists verify the diagnosis.
Authors: Shu-Hui Wang, Xin-Jun Han, Jing Du, Zhen-Chang Wang, Chunwang Yuan, Yinan Chen, Yajing Zhu, Xin Dou, Xiao-Wei Xu, Hui Xu & Zheng-Han Yang