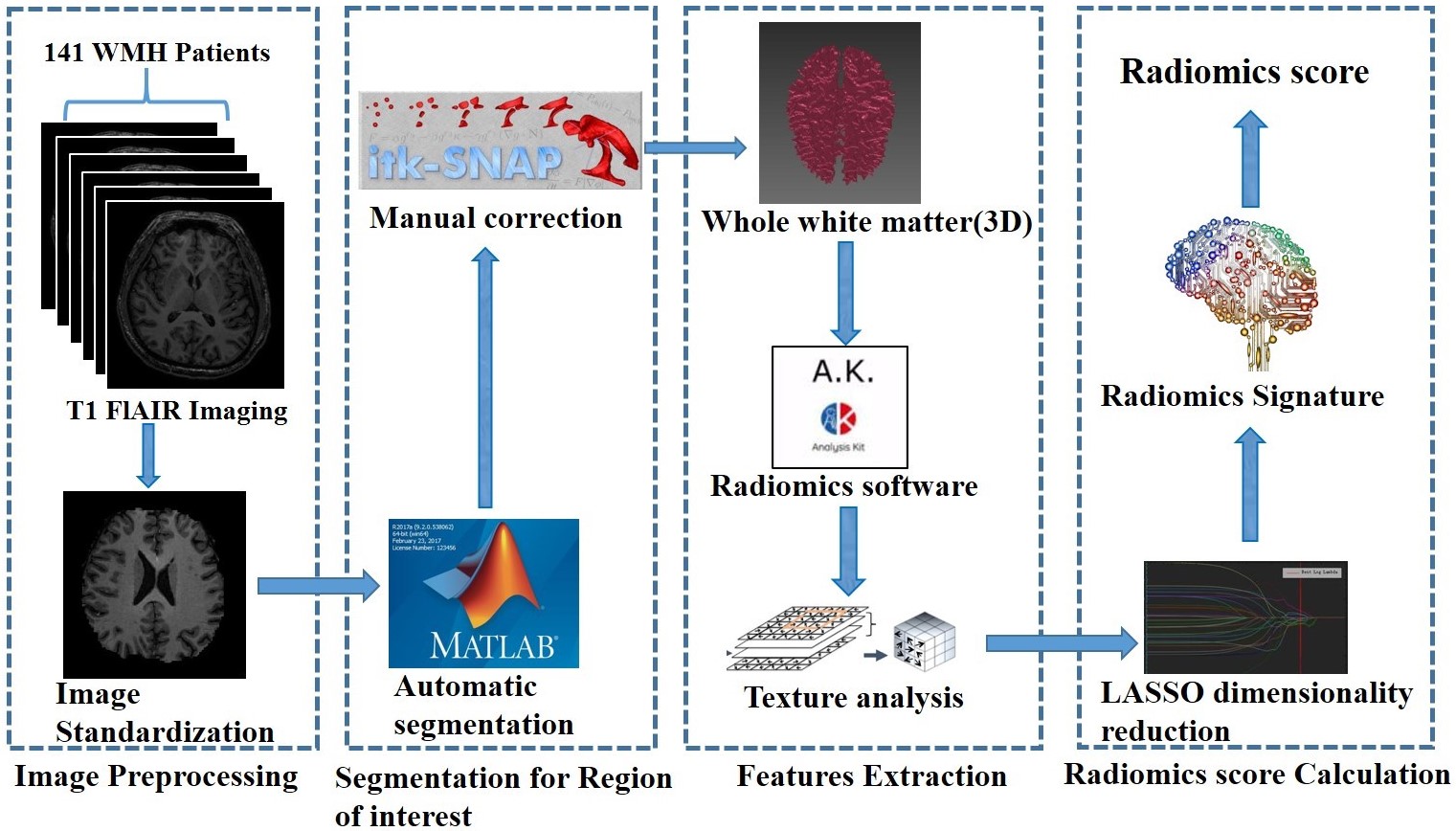
As a research hotspot in recent years, radiomics provides a new perspective for image diagnosis or evaluation by mining a large number of non-traditional visual information in medical images and adds new indicators (image markers). Radiomics may become a non-invasive, low-cost and easy to popularize imaging tool. White matter hyperintensity (WMH) refers to the high signal of white matter area on T2WI or flair MRI images. It is a common finding of brain MRI in the elderly and it is an important part of cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD). WMH is a growing pathological change in an ageing society. It is considered to be a risk factor for cognitive decline, dementia, depression, stroke, gait and balance problems.
In the present study, we used radiomics to predict the progress of WMH and the related risk factors, hoping to find a way for early detection and early diagnosis of WMH, and provide a time window for early intervention, containment, and slowing down the progress of white matter. Based on our study, we conclude that radiomics can well predict the progression of white matter lesions and age, blood lipid, and BMI are the main factors for the progression of white matter lesions. In conclusion, radiomics based on brain MRI is expected to be a useful tool for early identification and prediction of WMH progression. Early intervention strategies such as controlling blood lipid and lowering BMI may reduce the occurrence, and delay the progression, of WMH.
Key points
- Radiomics features detected by magnetic resonance imaging may be used to predict the progression of white matter hyperintensities.
- Radiomics may be used to identify risk factors associated with the progression of white matter hyperintensities.
- Radiomics may serve as non-invasive biomarkers to monitor white matter status.
Authors: Zhenyu Shu, Yuyun Xu, Yuan Shao, Peipei Pang & Xiangyang Gong