The aim of this retrospective study was to develop non-invasive machine learning (ML) classifiers for predicting post-Glenn shunt patients with low and high risks of a mean pulmonary arterial pressure above 15 mmHg, which was based on pre-operative cardiac CT. The study included 96 patients who underwent a bidirectional Glenn procedure.
Key points
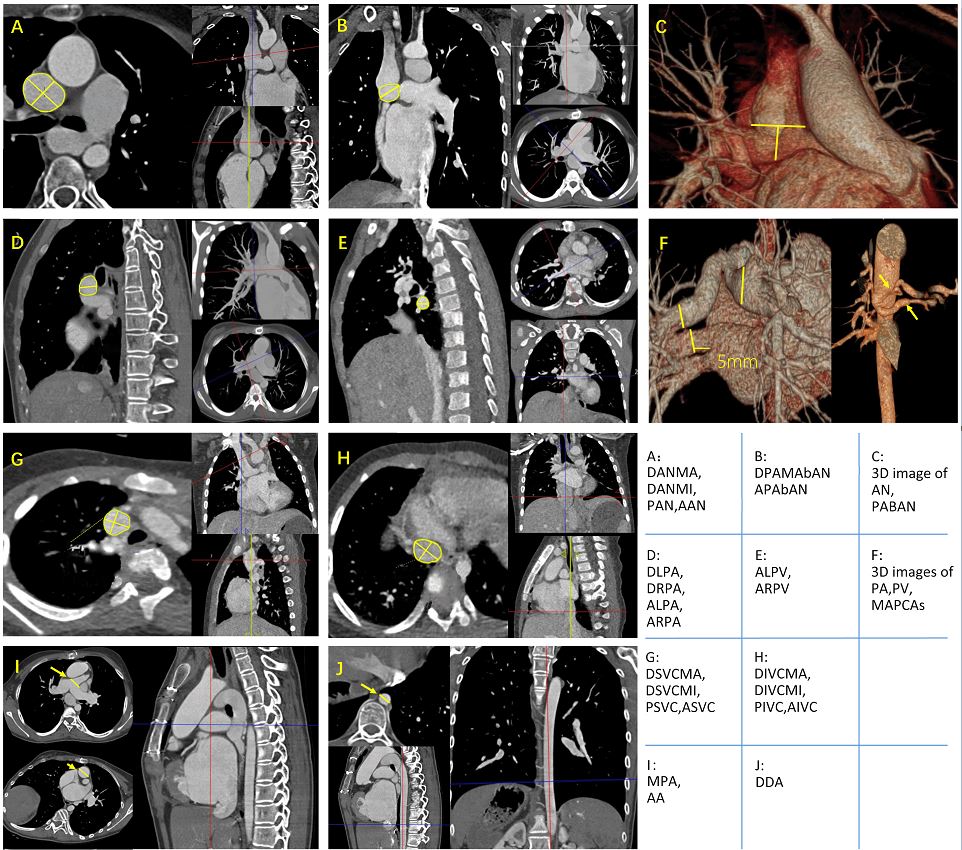
- Twenty-three candidate descriptors were manually extracted from cardiac computed tomography images, and seven of them were selected for subsequent modeling.
- The random forest model presents the best predictive performance for pulmonary pressure among all methods.
- The computed tomography-based machine learning model could predict post–Glenn shunt pulmonary pressure non-invasively.
Authors: Lei Huang, Jiahua Li, Meiping Huang, Jian Zhuang, Haiyun Yuan, Qianjun Jia, Dewen Zeng, Lifeng Que, Yue Xi, Jijin Lin & Yuhao Dong