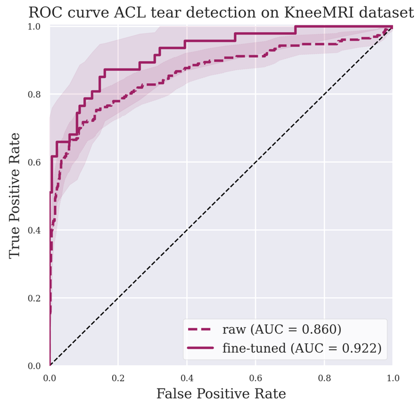
The purpose of this study was to develop a deep-learning algorithm for tear detection in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), subsequently comparing its accuracy using two external datasets. The authors were able to conclude that their algorithm was capable of showing high performance in the detection of ACL tears.
Key points
- An algorithm for detecting anterior cruciate ligament ruptures was built from a large dataset of nearly 20,000 MRI with AUC values of 0.939, sensitivity of 87%, and specificity of 91%.
- This algorithm was tested on two external populations from different other countries: a dataset from an American population and a dataset from a Croatian population. Performance remains high on these two external validation populations (AUC of 0.962 and 0.922 respectively).
Authors: Alexia Tran, Louis Lassalle, Pascal Zille, Raphaël Guillin, Etienne Pluot, Chloé Adam, Martin Charachon, Hugues Brat, Maxence Wallaert, Gaspard d’Assignies & Benoît Rizk