Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) carries a dismal prognosis. For a decade, sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor, was the only approved systemic therapy for HCC. However, its response rate in advanced HCC is only about 2%. The last few years have seen rapid approval of additional systemic therapies for HCC, including immunotherapy strategies. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab has a promising reported response rate of 20% in advanced HCC. With the emerging role of targeted therapies for advanced HCC, it also becomes increasingly relevant to accurately characterize HCC lesions in order to allow for patient-specific treatment selection. Many sophisticated techniques, including those involving immunophenotyping and genomics evaluation, have been developed. However, these methods all require invasive tissue sampling and specialized equipment and expertise.
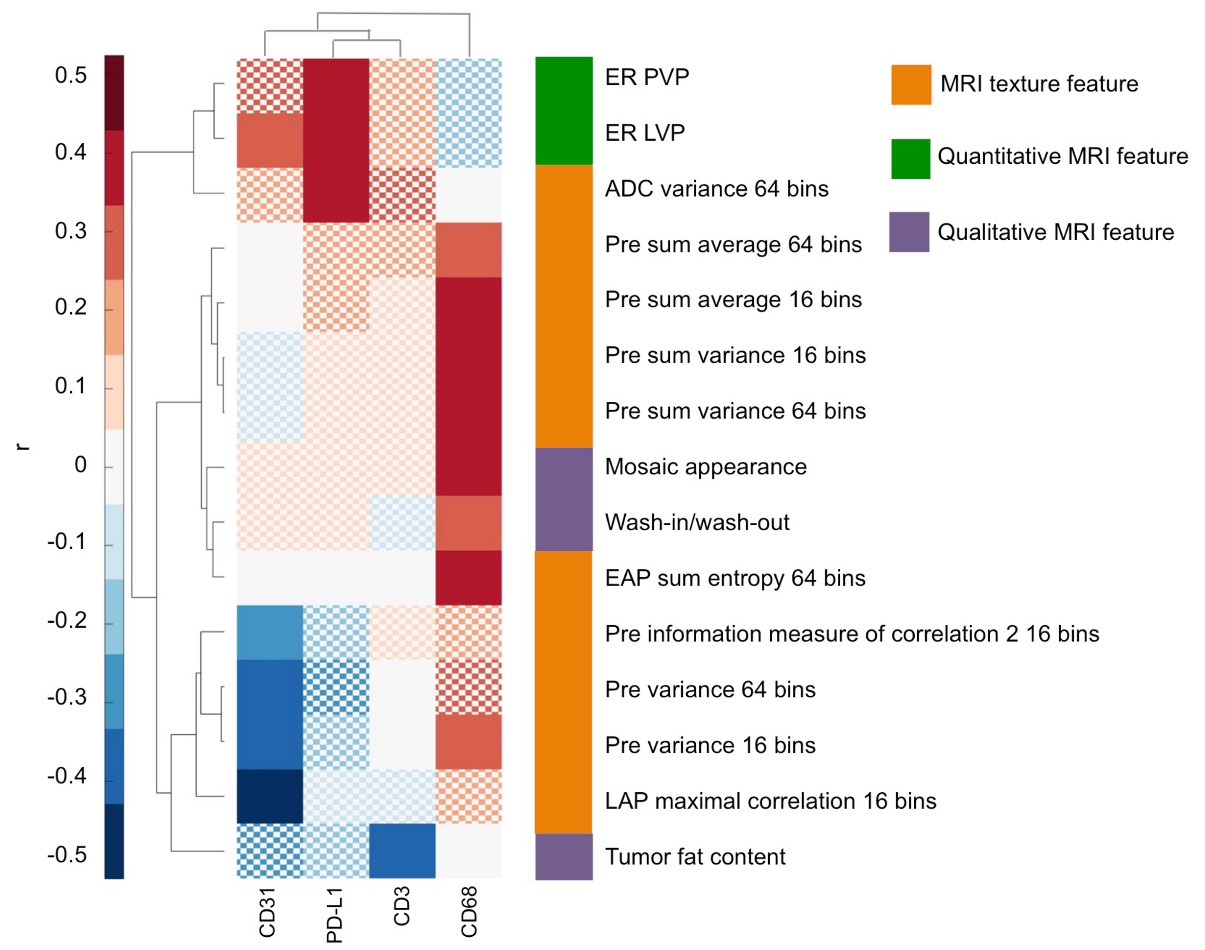
In our study, we aimed to evaluate the potential role of MRI radiomics features as surrogate noninvasive biomarkers for immuno-oncological characteristics of HCC. Radiomics is an emerging field in medical imaging, in which it is recognized that quantitative imaging features extracted from diagnostic images may be correlates of the underlying tissue biology. In our retrospective analysis of resected HCC patients with MRI performed before surgery, we found that MRI radiomics features showed significant correlation with histopathological immunophenotyping markers, including protein expression of CD3 (T-cells) and immunotherapy target PD-L1. We also found numerous significant correlations of radiomics features with RNA expression levels, including expression of immune checkpoint inhibitors PD-1 and CTLA4.
Thus, our results suggest a promising role of MRI radiomics analysis for prediction of immune-oncological features of HCC. While these results need further validation in larger and external cohorts, our study may pave a path toward personalized treatment stratification of HCC lesions using non-invasive imaging.
Key points
- MRI radiomics features showed significant associations with immunophenotyping and genomics characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Radiomics features, including tumour size, showed significant associations with early hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after resection.
Article: MRI radiomics features predict immuno-oncological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
Authors: Stefanie J. Hectors, Sara Lewis, Cecilia Besa, Michael J. King, Daniela Said, Juan Putra, Stephen Ward, Takaaki Higashi, Swan Thung, Shen Yao, Ilaria Laface, Myron Schwartz, Sacha Gnjatic, Miriam Merad, Yujin Hoshida & Bachir Taouli