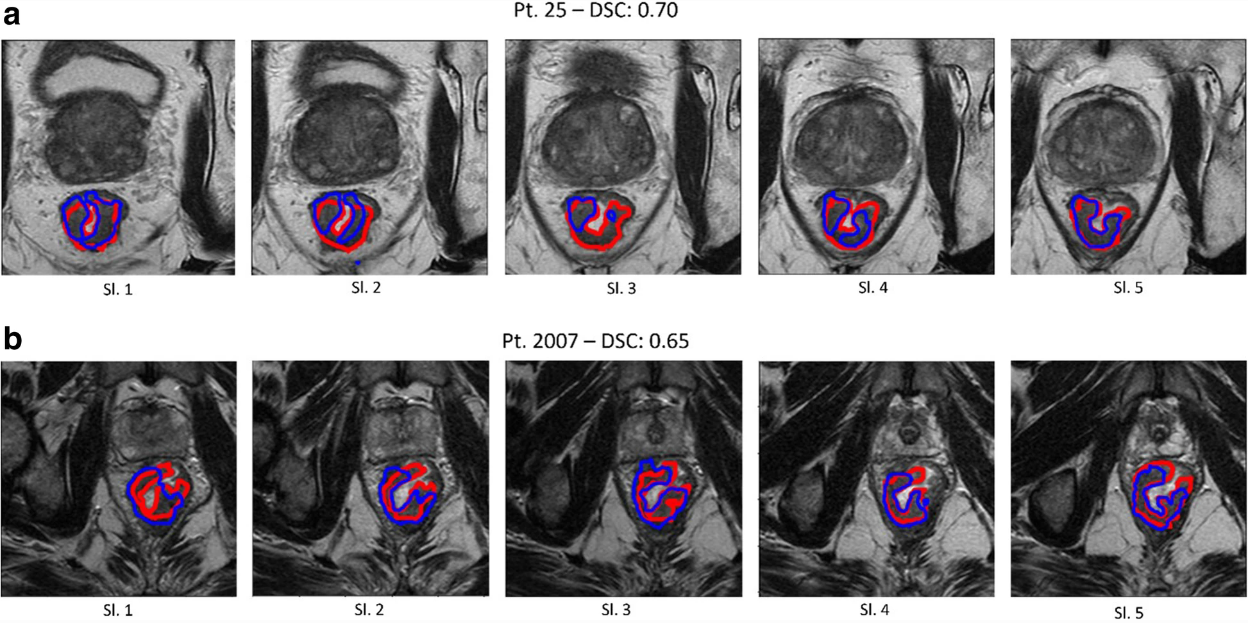
The study aimed to implement and externally validate an MRI-based radiomics pipeline in order to predict the response to treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), while also investigating the impact of manual and automatic segmentations on said radiomics models. The authors were able to show that radiomics models can help clinicians in the prediction of tumor response to chemoradiotherapy concerning LARC and assist in personalizing patient treatment.
Key points
- We implemented and validated a promising radiomics model to predict response of locally advanced rectal cancers (LARC) to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in a multicentre dataset.
- To provide a robust model for further clinical applications, we externally validated the model, using patients from a different centre, who underwent magnetic resonance imaging with various scanners and protocols.
- Results on both training and validation datasets were promising and showed that the model could be generalisable.
- Automatic segmentations reached a significantly higher accuracy on the validation set, compared to the manual segmentation, prompting the use of the automatic pipeline on a larger validation cohort.
Authors: Arianna Defeudis, Simone Mazzetti, Jovana Panic, Monica Micilotta, Lorenzo Vassallo, Giuliana Giannetto, Marco Gatti, Riccardo Faletti, Stefano Cirillo, Daniele Regge & Valentina Giannini