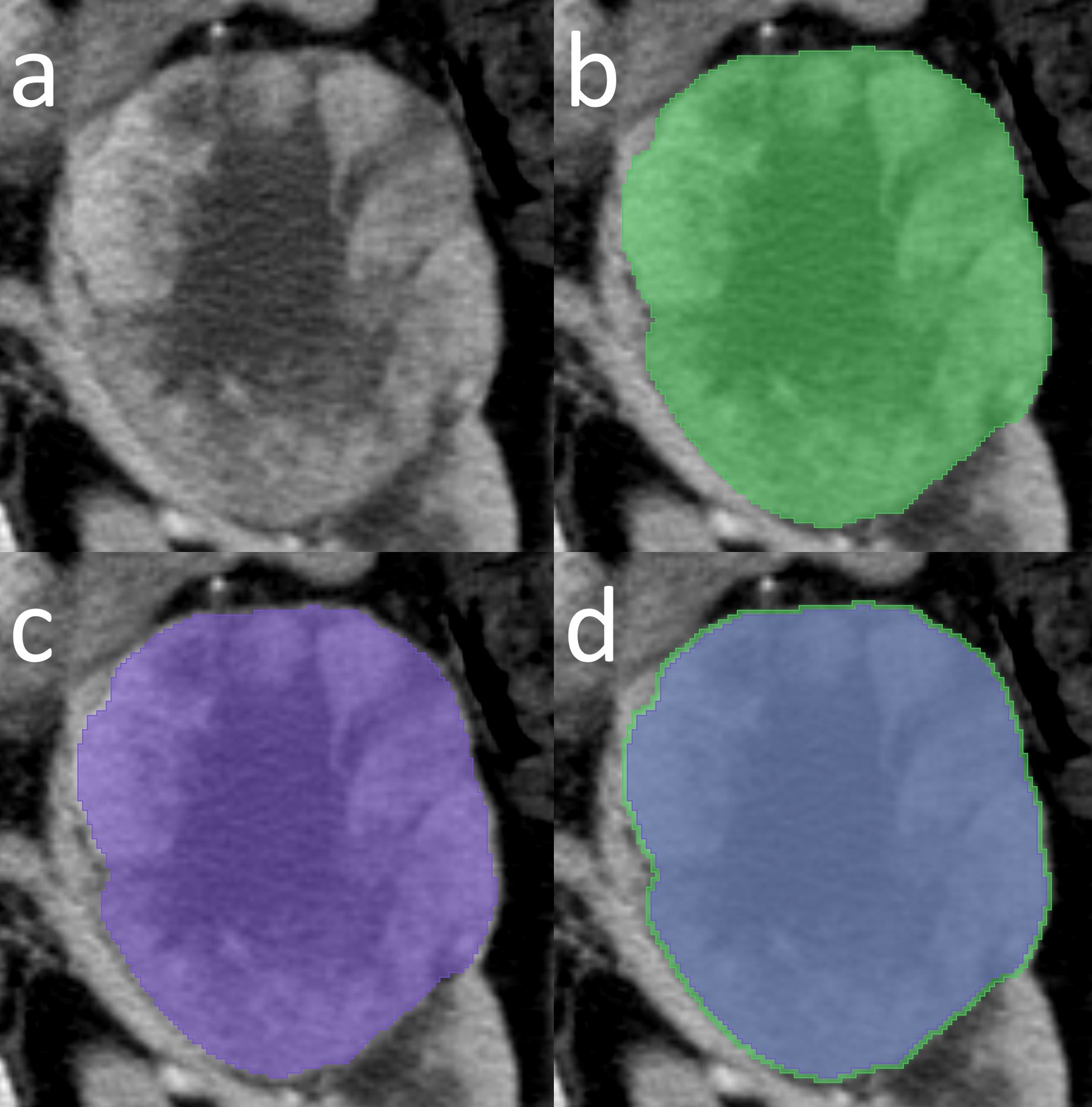
Radiomic workflows include various challenging steps. One of the most demanding steps in radiomics is the segmentation process. Particularly for the renal cell carcinomas, most of the studies used manual tumour contour delineation. In this work, our group wanted to perform an experiment by changing the segmentation margin a little bit, that is, just 2 mm, to see what happens throughout every step thereafter. We strictly preserved the nature of the data in this experiment, such as cross-validation folds, seed, and so on. We found that each step of a machine learning (ML)-based high-dimensional quantitative computed tomography texture analysis (qCT-TA) was very sensitive to even a slight change of 2 mm in segmentation margin. Despite yielding fewer texture features with excellent reproducibility, performing the segmentation focusing on the outermost boundary of the tumours provided better classification performance in ML-based qCT-TA of renal clear cell carcinomas for distinguishing nuclear grade. Although it may seem contradictory, this could be related to the quality of the information that the texture feature included in the contour-focused segmentation. In summary, findings of an ML-based high-dimensional qCT-TA may not be reproducible in clinical practice, even using the same feature selection algorithm and ML classifier, unless the possible influence of the segmentation margin is considered. We think that future research should focus on the development of highly reproducible segmentation methods for renal cell carcinomas.
Key Points
- Each step of a machine learning (ML)-based high-dimensional quantitative computed tomography texture analysis (qCT-TA) is sensitive to even a slight change of 2 mm in segmentation margin.
- Despite yielding fewer texture features with excellent reproducibility, performing the segmentation focusing on the outermost boundary of the tumours provides better classification performance in ML-based qCT-TA of renal clear cell carcinomas for distinguishing nuclear grade.
- Findings of an ML-based high-dimensional qCT-TA may not be reproducible in clinical practice even using the same feature selection algorithm and ML classifier unless the possible influence of the segmentation margin is considered.
Authors: Burak Kocak, Ece Ates, Emine Sebnem Durmaz, Melis Baykara Ulusan, Ozgur Kilickesmez