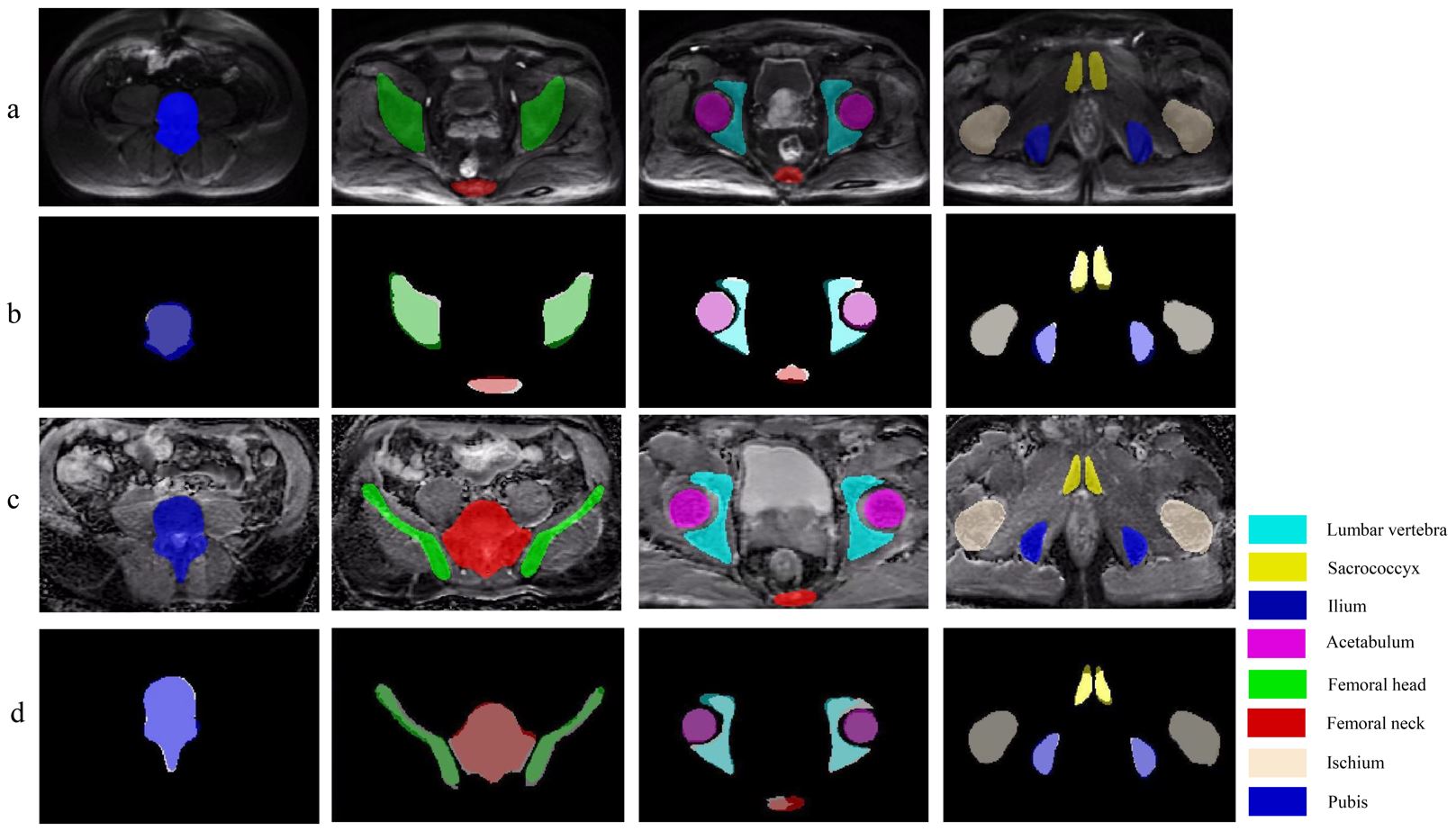
The accurate skeleton segmentation with their semantic labels represents the initial step to achieve accurate prostate cancer bone metastases detection on DWI and ADC images. Several studies have reported convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the segmentation of normal bone structures on CT images and bone scans; however, only a few studies on automatic segmentation of normal bone structures on MR images are available.
Here, we developed a 3D U-Net model to automatically segment different pelvic bony structures on DWI and ADC images—lumbar vertebra, sacrococcyx, ilium, acetabulum, femoral head, femoral neck, ischium, and pubis, and tested its feasibility quantitively and qualitatively. Our results showed that the 3D U-Net can achieve automated pelvic bone segmentation on DWI and ADC images with suitable quantitative and qualitative performance, which may provide essential localization information for subsequent research on pelvic bone metastases.
Key points
- 3D U-Net exhibits good performance for segmentation of normal pelvic bones.
- A SCORE system was designed for the qualitative evaluation of segmentation.
- It lays a foundation for the detection of pelvic bony metastases.
Authors: Xiang Liu, Chao Han, He Wang, Jingyun Wu, Yingpu Cui, Xiaodong Zhang & Xiaoying Wang