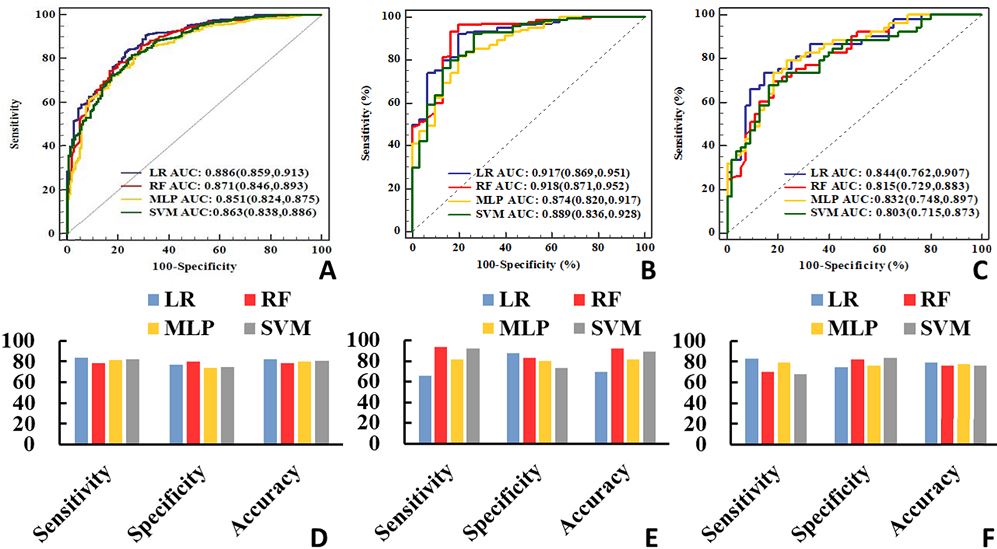
Decisions regarding the optimal management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) depend on a comprehensive comparison of the risks between aneurysm rupture and interventional treatment. The accurate prediction for UIA rupture risk is important for clinicians and patients. Our study further proves that the hemodynamic parameters can improve prediction performance for rupture status of UIAs. Moreover, the AUC of model integrating clinical, aneurysm morphological and hemodynamic parameters is 0.886, which can provide relatively accurate risk assessment and may help choose the optimal management. However, our study shows that machine learning (ML) methods can not outperform conventional logistic regression (LR) in prediction models for rupture status of UIAs integrating clinical, aneurysm morphological and hemodynamic parameters. Our study is retrospective and the aim of this model is to assess rupture status of UIAs. Hence, we feel that further research based on the nature of UIAs are needed to demonstrate the role of AI in the prediction of UIA rupture risk.
Key points
- The addition of hemodynamic parameters can improve prediction performance for rupture status of unruptured intracranial aneurysms.
- Machine learning algorithms cannot outperform conventional logistic regression in prediction models for rupture status integrating clinical, aneurysm morphological, and hemodynamic parameters.
- Models integrating clinical, aneurysm morphological, and hemodynamic parameters may help choose the optimal management.
Authors: Guozhong Chen, Mengjie Lu, Zhao Shi, Shuang Xia, Yuan Ren, Zhen Liu, Xiuxian Liu, Zhiyong Li, Li Mao, Xiu Li Li, Bo Zhang, Long Jiang Zhang & Guang Ming Lu