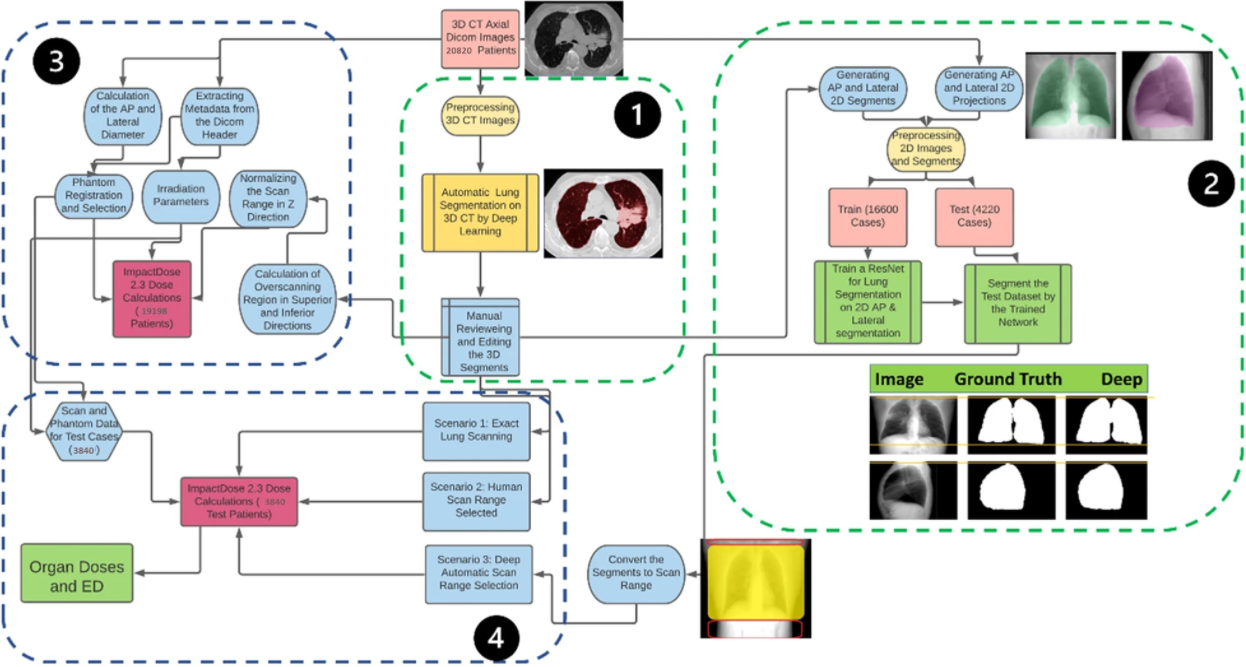
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of chest CT examinations has dramatically increased, which will undeniably impact public medical exposure. Overscanning, i.e., scanning unnecessary regions in the axial field-of-view, causes noticeable excessive radiation dose to patients undergoing chest CT examinations. The manual procedure of selecting the scan range based on anterior-posterior or lateral localizers is prone to human error in most cases.
In this work, we developed an automated workflow for task-specific scan range selection and retrospective evaluation of overscanning on a large cohort of a multi-centric and multi-purpose clinical database consisting of 20,820 thoracic CT examinations. The impact of overscanning on patients’ effective dose was investigated through personalized dosimetry of the considered cohort. A deep learning-assisted segmentation of the lungs was adopted through lung segmentation on the localizer images to enable choosing the exact scan range to optimize patients’ radiation dose associated with CT examinations. We evaluated our methodology with respect to accuracy in range selection and radiation dose reduction.
A significant overscanning range (31±24) mm was observed in a clinical setting for over 95% of the cases; more considerable in the inferior direction. Our proposed method’s error was -0.7±4.08 and 0.01±14.97 mm for superior and inferior directions, respectively. The evaluation of a sizeable multi-centric chest CT dataset revealed an unnecessary effective dose (ED) of more than two mSv per scan and a 67% increase in the thyroid absorbed dose, which can be eliminated by excluding unjustified body parts from the CT scan range employing this automated deep learning (DL) based method.
Key points
- Overscanning is a common problem (more than 95% of the cases) occurring mostly in the inferior direction in clinical practice, leading to additional unnecessary radiation dose in chest CT.
- We developed an accurate and robust automated method for scan range delimitation trained on a large dataset with acceptable reproducibility.
- Our proposed deep learning-guided algorithm could potentially reduce patient’s radiation dose by up to 21%.
Authors: Yazdan Salimi, Isaac Shiri, Azadeh Akhavanallaf, Zahra Mansouri, Abdollah Saberi Manesh, Amirhossein Sanaat, Masoumeh Pakbin, Dariush Askari, Saleh Sandoughdaran, Ehsan Sharifipour, Hossein Arabi & Habib Zaidi