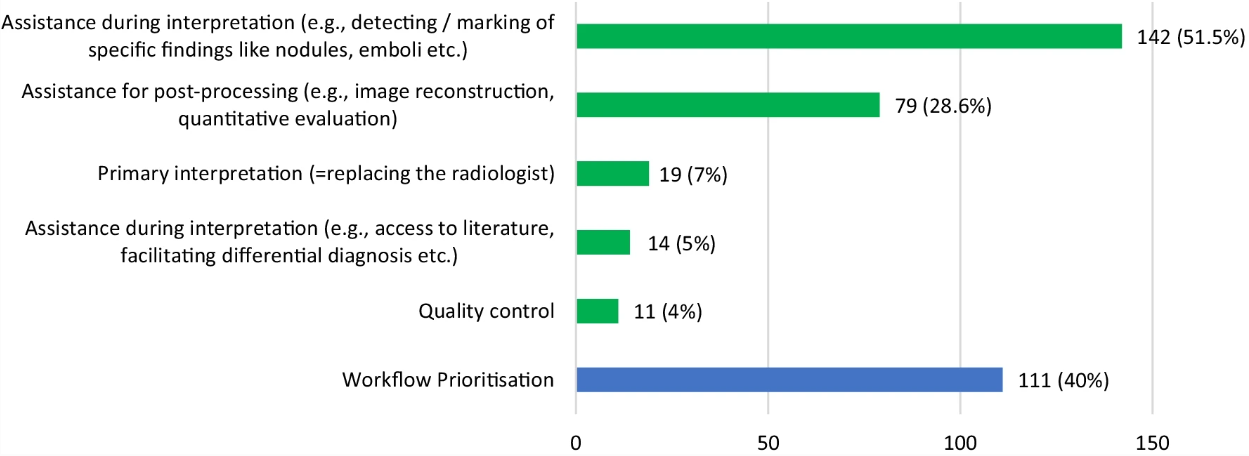
To obtain an impression of the current practical clinical experience of radiologists from different European countries with artificial intelligence (AI)-powered tools, the European Society of Radiology (ESR) conducted a survey among its members. Out of a total of 690 respondents, there were 276 radiologists from 229 institutions in 32 countries who responded that they had practical clinical experience with an AI-based algorithm either at academic institutions (52%), in regional hospitals (37%) or in private practice (11%). When used for diagnostic purposes, the algorithms were considered generally reliable by 75.7% of users; only 17.8% experienced technical difficulties regarding the integration of these tools into their workflow. However, only 42 (22.7%) experienced a significant reduction in their workload, whereas 129 (69.8%) found that there was no such effect. When used for clinical workflow prioritisation, AI algorithms were found to be very helpful in reducing the workload by 23.4% of the respondents, but only moderately helpful by 62.2% or not helpful at all by 14.4%.
Compared with initial predictions and expectations, the overall impact of AI-based algorithms on current radiological practice in Europe appeared rather modest. Similar observations were made in a recent survey of North American radiologists by the American College of Radiology (ACR).
The ESR survey indicates that most radiologists experienced no practical clinical workload reduction. Future observations should focus on the specific use cases in which AI-powered tools are most likely to have a time–saving effect, e.g. those with low diagnostic complexity and with a high case volume.
Key points
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms are being used for a large spectrum of use case scenarios in clinical radiology in Europe, including assistance with interpretive tasks, image post-processing, and prioritisation in the workflow.
- Most users considered AI algorithms generally reliable and experienced no major problems with technical integration in their daily practice.
- Only a minority of users experienced a reduction of the workload of the radiological medical staff due to the AI algorithms.
Authors: Christoph D. Becker, Elmar Kotter, Laure Fournier, and Luis Marti-Bonmati, European Society of Radiology (ESR)