Technological advancements in healthcare have raised our standard of care, but at the same time raised the costs to deliver that care. This trend forces us to be critical about the added value (health benefit and/or reduced costs) of any new technology we bring in, also for AI software.
Health economic evaluations can help in assessing the (potential) value of AI but are still very scarce. The authors of a recent review could so far only identify two health economic studies on radiology AI, while almost 200 commercial products are available for the European market.
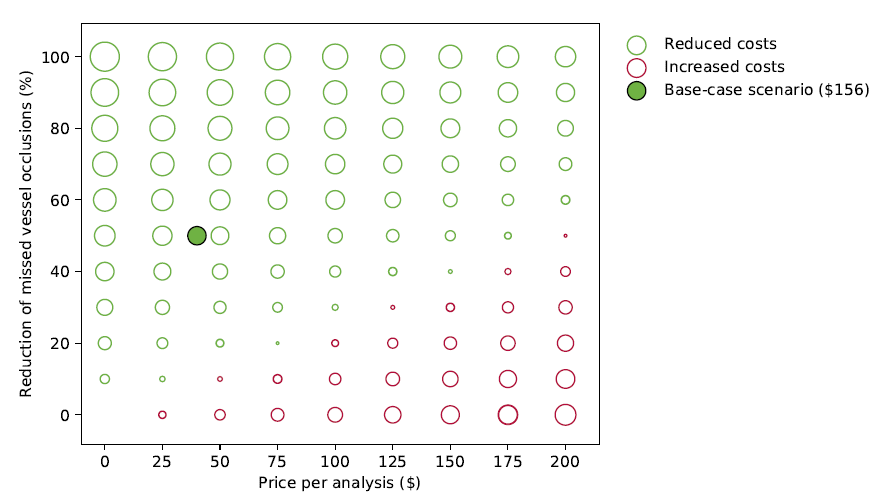
That would make our study the third for radiology AI. As we were interested in using AI to aid radiologists in the diagnosis of stroke patients by detecting large vessel occlusions (LVOs), we decided to perform an early health technology assessment (HTA). Early HTA aims to model the potential cost-effectiveness of an innovation before implementing it in clinical practice. This allows us, before investing in such a product, to estimate its potential clinical and monetary value.
Our study showed that in many scenarios an AI tool for LVO detection on CTA is potentially cost-effective (dependent on AI performance levels, price, and missed occlusion rate). It also demonstrated that the reduced costs and increased health are long-term outcomes, while in the short term the innovation may be more costly than the standard of care without AI. As such, the costs and benefits end up at different stakeholders (e.g. radiology vs. neurology, inside and outside the hospital). These observations could contribute to the debate on the investments, financial accountability, and reimbursement for the clinical use of AI technology.
We have made the Excel model publicly available, so you can play around with the input variables of the model and easily adapt it to your own situation. The model and further details can be found in our blog post.
Key points
- Early health technology assessment can be used to assess impact of AI.
- The use of AI for large vessel occlusion detection may be cost-effective.
- Increased health and costs savings are expected over the projected lifetime.
- Financial investments and benefits are allocated differently, challenging adoption.
Authors: Kicky G. van Leeuwen, Frederick J. A. Meijer, Steven Schalekamp, Matthieu J. C. M. Rutten, Ewoud J. van Dijk, Bram van Ginneken, Tim M. Govers & Maarten de Rooij