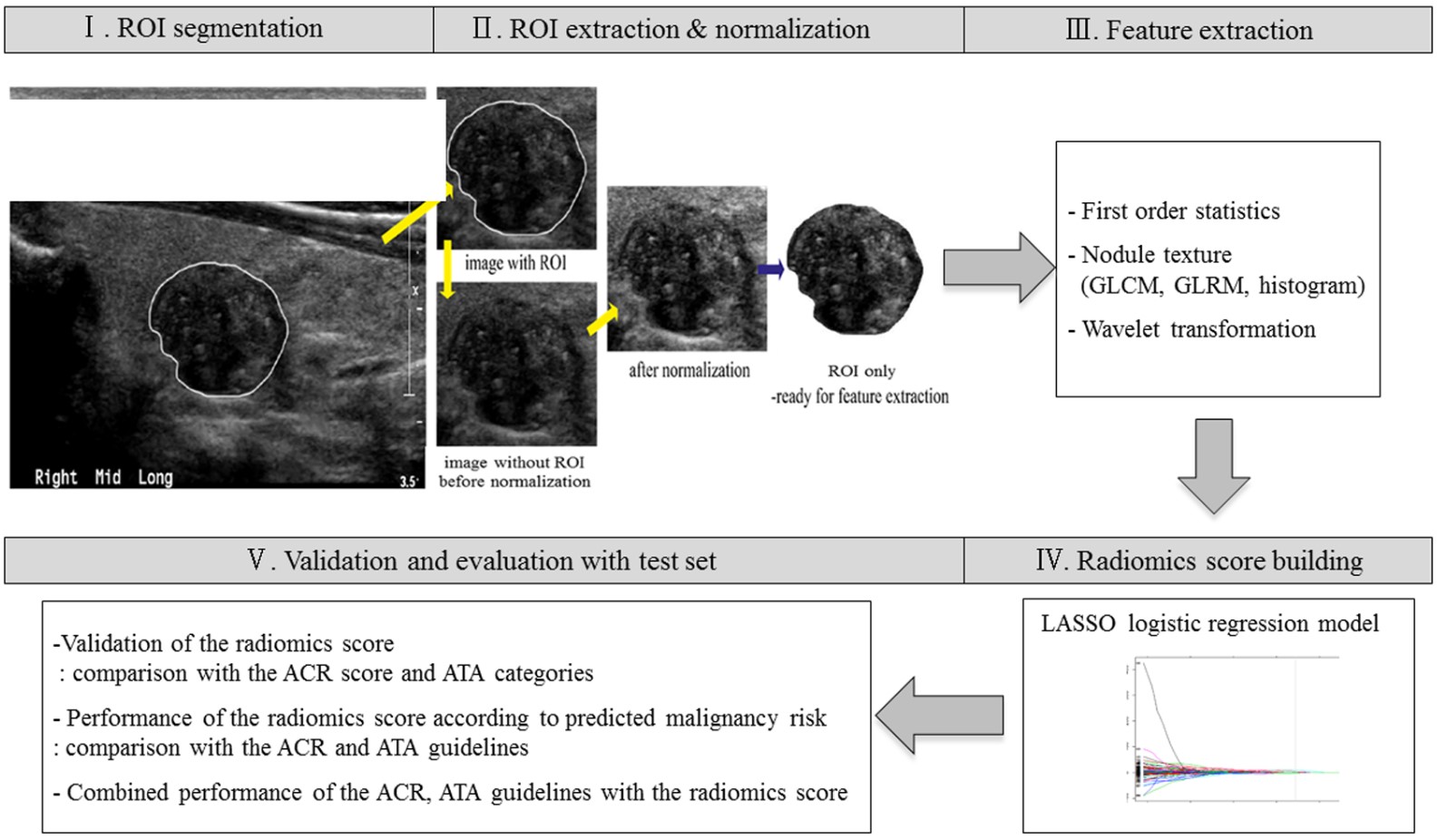
In this study, the authors develop a radiomics score using ultrasound images in order to predict thyroid malignancy and to investigate its potential as a complementary tool to improve the performance of risk stratification systems. They found that radiomics was able to help predict malignancy in thyroid nodules in combination with risk stratification systems by improving specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), and unnecessary fine-needle aspiration (FNA) rates while maintaining sensitivity of the ACR and ATA guidelines for expert and non-expert readers.
Key points
- The radiomics score yielded an AUC of 0.85 and 0.75 in the training and test set, respectively.
- For all readers, combining a 5% predicted malignancy risk cutoff for the radiomics score with the ACR and ATA guidelines significantly increased specificity, accuracy, and PPV and decreased unnecessary FNA rates, with no decrease in sensitivity.
- Radiomics can help predict malignancy in thyroid nodules in combination with risk stratification systems, by improving specificity, accuracy, and PPV and unnecessary FNA rates while maintaining sensitivity for both expert and nonexpert readers.
Authors: Vivian Y. Park, Eunjung Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Hye Jung Kim, Jiyoung Yoon, Jinwoo Son, Kijun Song, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Ga Ram Kim & Jin Young Kwak