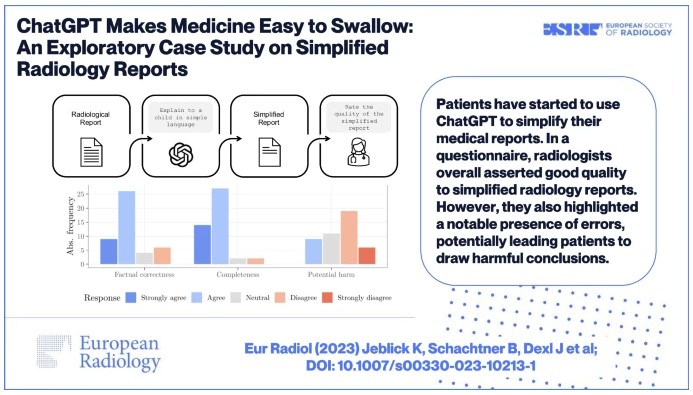
Just over a year ago, the release of ChatGPT marked a turning point in AI and language processing, sparking widespread excitement for Large Language Models (LLMs) for diverse use cases across various domains. Back then, we noticed friends using ChatGPT for medical text simplification, yet, as medical laypersons, they couldn’t verify the accuracy of the simplified text. Anticipating its imminent adoption by patients, we felt compelled to explore the challenges and opportunities of this emerging phenomenon. We therefore designed an exploratory case study to carry out a first scientific assessment of the quality of radiology reports simplified with ChatGPT, focusing on factual correctness, completeness, and potential harm.
Results revealed that while most participating radiologists overall asserted good quality to radiology reports simplified with ChatGPT, they also highlighted a notable presence of errors, from which patients might draw harmful conclusions. We concluded that further adaptation of LLMs to the healthcare domain and supervision by experts are needed to minimize this risk.
Envisioning the future, we propose integrating ChatGPT-like LLMs directly into clinics or radiology centers to increase patient autonomy; alongside the original radiology report, a simplified report would be automatically generated for the patient with a ChatGPT-like LLM and undergo review by a radiologist, ensuring corrections where necessary.
Building on our findings and subsequent studies released by other researchers, we believe that LLMs like ChatGPT hold vast potential for advancing patient-centered care in radiology and other medical domains.
Key points
- Patients have started to use ChatGPT to simplify their medical reports, but their quality was unknown.
- In a questionnaire, most participating radiologists overall asserted good quality to radiology reports simplified with ChatGPT. However, they also highlighted a notable presence of errors, potentially leading patients to draw harmful conclusions.
- Large language models such as ChatGPT have vast potential to enhance patient-centered care in radiology and other medical domains. To realize this potential while minimizing harm, they need supervision by medical experts and adaption to the medical field.
Article: ChatGPT makes medicine easy to swallow: an exploratory case study on simplified radiology reports
Authors: Katharina Jeblick, Balthasar Schachtner, Jakob Dexl, Andreas Mittermeier, Anna Theresa Stüber, Johanna Topalis, Tobias Weber, Philipp Wesp, Bastian Oliver Sabel, Jens Ricke & Michael Ingrisch