Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common complication in patients with cancer. A significant number of all PE are diagnosed incidentally (incidental PE, iPE) in CT scans performed for staging or treatment response evaluation. Thousands of CT scans are performed for this indication every year in Halmstad, a regional hospital in Region Halland in southern Sweden, and we anticipate that in a few percent of the examinations there is an iPE. However, these scans are not optimized for assessing the pulmonary arteries and there’s a risk that the pulmonary arteries are not systematically assessed during reading, increasing the risk that an iPE is overlooked.
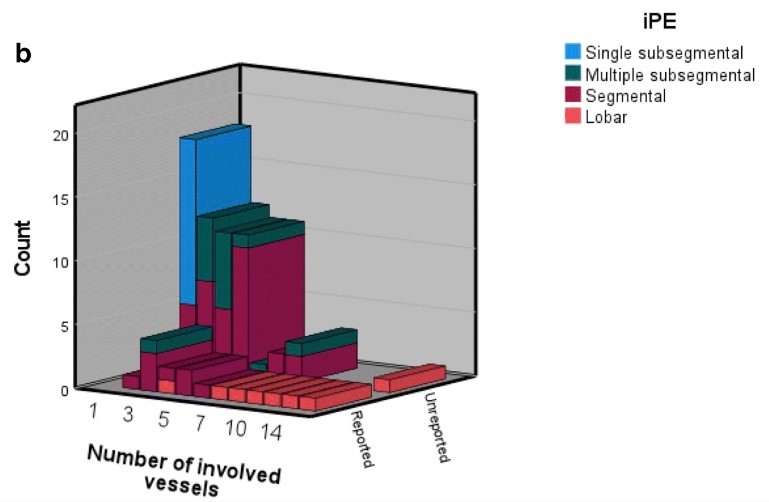
We wanted to investigate the prevalence of reported and unreported iPE in patients with cancer, and to evaluate a commercially available AI algorithm for the detection and triage of iPE. In this study, all CT scans including the chest on patients with cancer during one year were retrospectively reviewed for the presence of iPE. The total iPE prevalence was 4.0% (75 iPE cases in 1892 CT studies), of which only 21% (16/75) were reported. While unreported iPE had a lower embolic burden, the majority were proximal to the subsegmental arteries. The AI algorithm correctly identified 68 of 75 iPE, with three false positives (sensitivity 90.7%, specificity 99.8%, PPV 95.6%, NPV 99.6%).
As the AI algorithm had high accuracy for iPE, it has the potential to increase the detection rate of iPE, and the low number of false positives is a prerequisite for easy integration in the clinical workflow. The AI algorithm has now been deployed in clinical routine in all three hospitals in Region Halland and is used in all contrast-enhanced CT scans including the chest. Our current research efforts are now focused on the clinical outcome of cancer patients with retrospectively identified unreported iPE, and the effects of using AI in clinical routine on iPE detection rate, report turnaround time, and time to treatment for patients with iPE.
Key points
- In a retrospective single-center study on patients with cancer, unreported iPE were common, with the majority lying proximal to the subsegmental arteries.
- The evaluated AI algorithm had a very high sensitivity and specificity, so has the potential to increase the detection rate of iPE.
Authors: Peder Wiklund, Koshiar Medson & Johan Elf