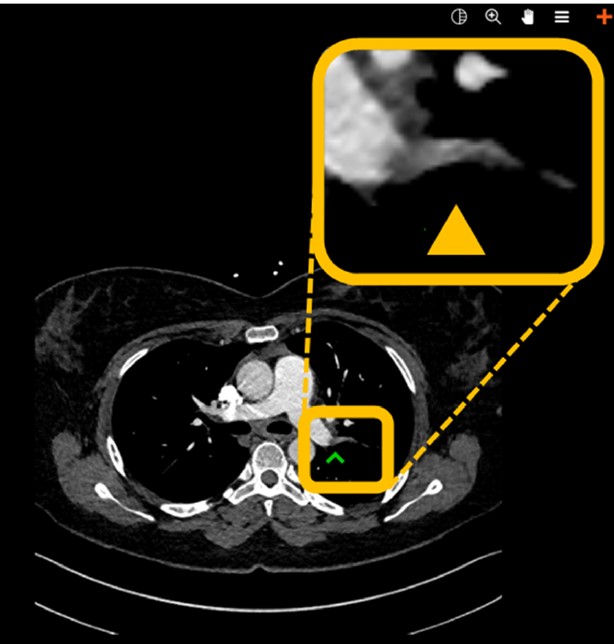
The detection of pulmonary embolism (PE) in CT pulmonary angiograms (CTPAs) is a great example of a major challenge radiologists face nowadays: The swift identification and communication of critical findings in times of sharply rising numbers of examinations performed. A potential auxiliary tool helping us to master the flood of information and separate signal (critical findings) from noise (unremarkable examinations) is algorithms that process examinations in the background and notify us in cases with suspected critical findings.
In our study, we evaluated the performance of a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for detection of PE using all CTPAs acquired at our institution, a university hospital, during a whole year. The algorithm based on ResNet architecture had been trained on more than 28,000 CTPAs from other institutions. Among others, we found a sensitivity of 92.7% and a specificity of 95.5% on a per-examination level, which makes it a valuable aide for radiologists.
While these kinds of performance checks on real clinical data are indispensable, they are just one of many steps to meaningful application of AI in radiology. Starting now, we should widen our focus and include two more aspects: First, how exactly do we integrate algorithm results in clinical workflows so they make lives of radiologists easier and don’t add extra workload. This is not only key for acceptance of AI, but also its practical implementability. At our department, we opted for a widget-based solution for the PE detection algorithm: A pop-up window occurs at the radiologist’s workstation whenever PE is suspected (and only then). It includes a key image of the suspected embolus- prompting direct reading of the case by a radiologist. And second, we need to take the impact on patient outcomes into account: the best performing algorithm is worthless if its results do not find their way to the right person at the right time.
Staying with our example, this means we need – among other things – to have a closer look at the influence of the algorithm on communication times to referring physicians. The work has just begun.
Key points
- An AI-based prototype algorithm showed a high degree of diagnostic accuracy for the detection of pulmonary embolism on CTPAs.
- It can therefore help clinicians to automatically prioritize exams with a high suspection of pulmonary embolism and serve as secondary reading tool.
- By complementing traditional ways of worklist prioritization in radiology departments, this can speed up the diagnostic and therapeutic workup of patients with pulmonary embolism and help to avoid false negative calls.
Article: Automated detection of pulmonary embolism in CT pulmonary angiograms using an AI-powered algorithm
Authors: Thomas Weikert, David J. Winkel, Jens Bremerich, Bram Stieltjes, Victor Parmar, Alexander W. Sauter & Gregor Sommer