Fractures in children are common, sometimes subtle and can signify underlying child abuse. They present unique challenges, given the different appearances of the growing skeleton at different ages. In this systematic review, the authors reviewed the available literature on the use of AI for paediatric fracture detection.
Additional Key points:
- Few articles (n=9) were available for review regarding paediatric fracture detection using AI.
- Most AI models focused on radiographic interpretation, with the elbow being the most common body part evaluated.
- Accuracy rates varied across different AI models from 88.8% to 97.9%. A table of diagnostic accuracies of the different models for different body parts is provided in Table 4 in main article.
- There were two articles where the AI performance was slightly higher than human readers, but this was not statistically significant.
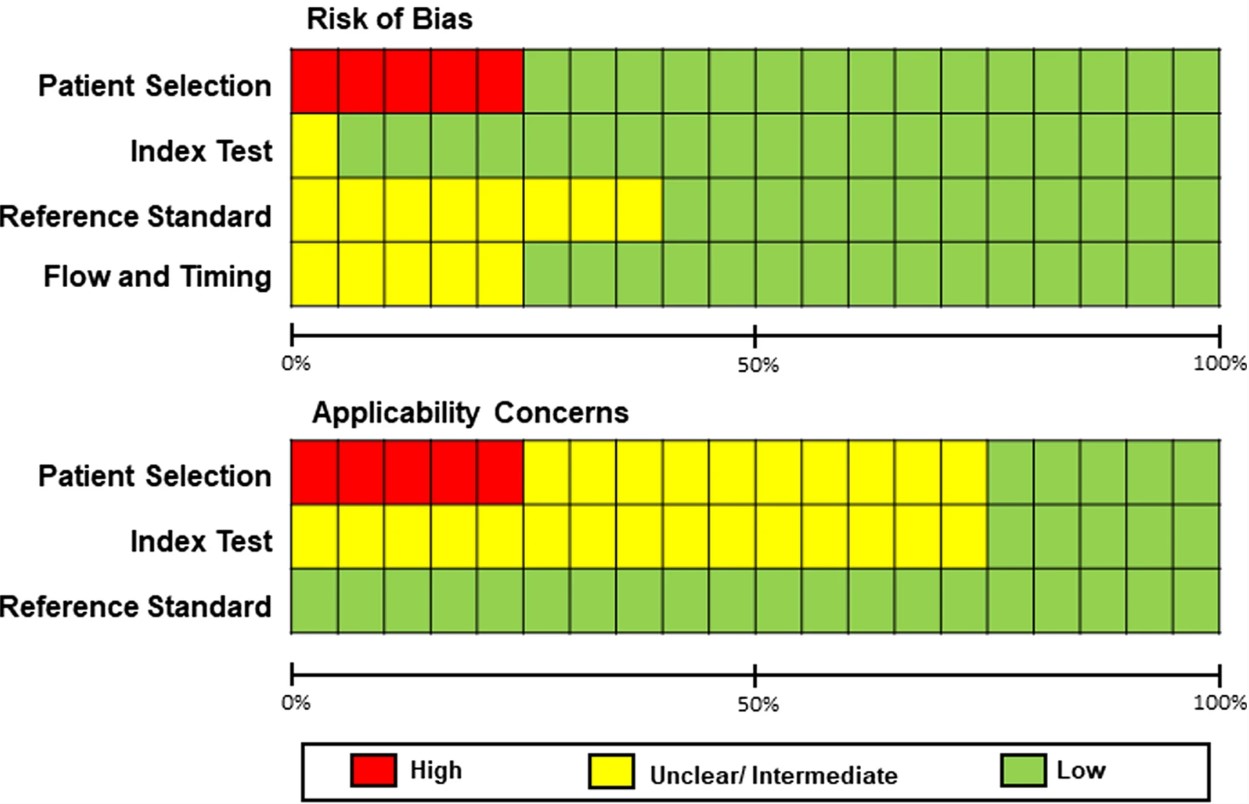
- Almost all published work was biased, with data arising from a single centre with only a minority performing any external validation.
In the authors’ opinion, the wide heterogeneity and limited information make the generalisation of AI performance to a wider population difficult. Future efforts should be made to collect multicentric data with external validation, to understand the real-world impact.
Key points
- Most artificial intelligence tools for fracture detection on children have focussed on plain radiographic assessment.
- Almost all eligible articles used training, validation and test datasets derived from a single institution.
- Strict inclusion and exclusion criteria for algorithm development may limit the generalisability of AI tools in children.
- AI performance was marginally higher than human readers, but not significantly significant.
- Opportunities exist for developing AI tools for very young children (< 2 years old), those with inherited bone disorders and in certain clinical scenarios (e.g. suspected physical abuse).
Article: Artificial intelligence for radiological paediatric fracture assessment: a systematic review
Authors: Susan C. Shelmerdine, Richard D. White, Hantao Liu, Owen J. Arthurs & Neil J. Sebire