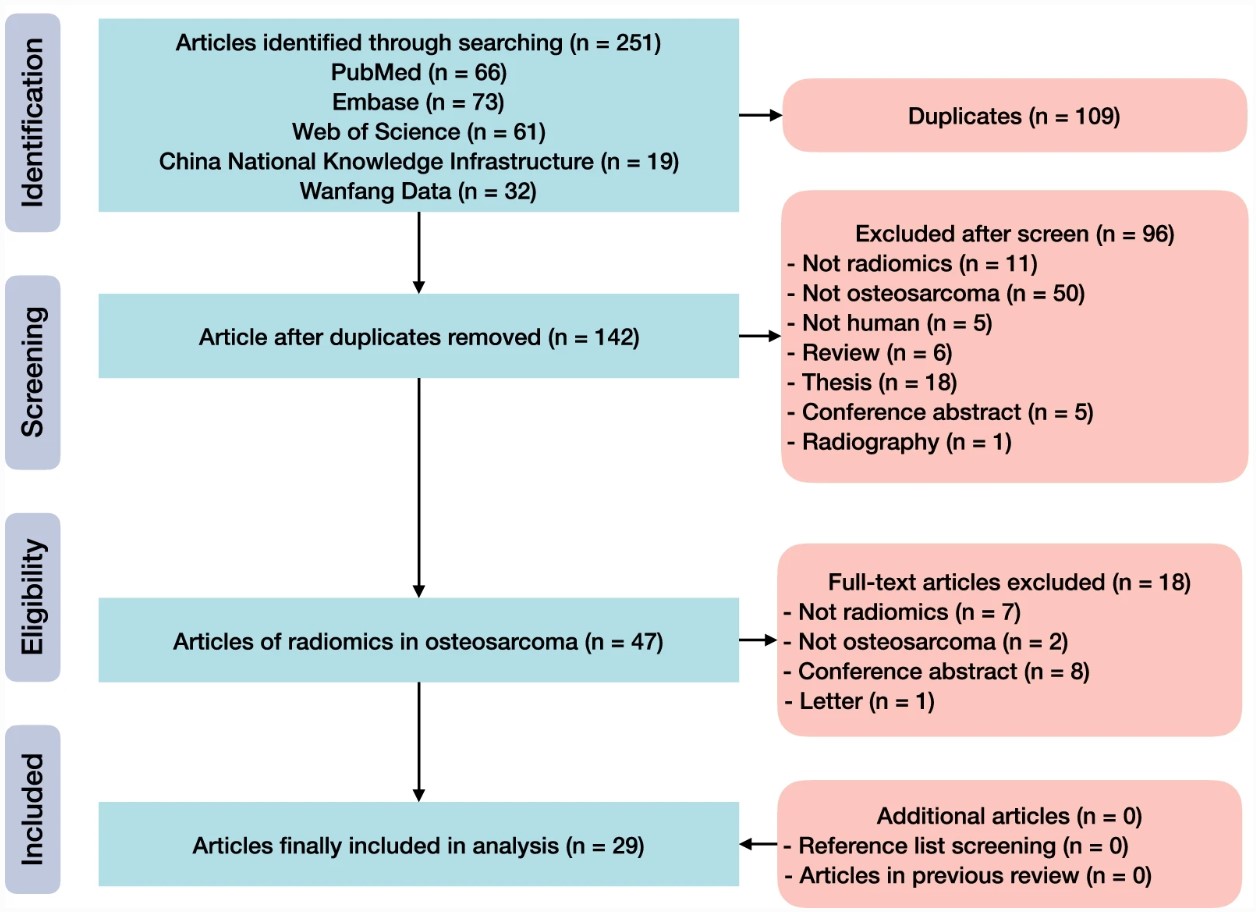
The aim of this study was to provide an updated systematic review of radiomics in osteosarcoma, utilizing various databases such as PubMed, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and more. Articles found in these databases were assessed by Radiomics Quality Score (RQS), Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD) statement, Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM), and modified Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) tool. The authors determined that the quality of osteosarcoma radiomics studies was lacking and more investigation needs to be done before using radiomics to enhance osteosarcoma treatment, while also finding that CLAIM is recommended for the reporting of radiomics research.
Key points
- The MRI-radiomics in predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response is supported by weak evidence.
- The quality of osteosarcoma radiomics studies has been improved recent two years.
- CLAIM can adapt the increasing trend of deep learning application in radiomics.
Authors: Jingyu Zhong, Yangfan Hu, Guangcheng Zhang, Yue Xing, Defang Ding, Xiang Ge, Zhen Pan, Qingcheng Yang, Qian Yin, Huizhen Zhang, Huan Zhang & Weiwu Yao